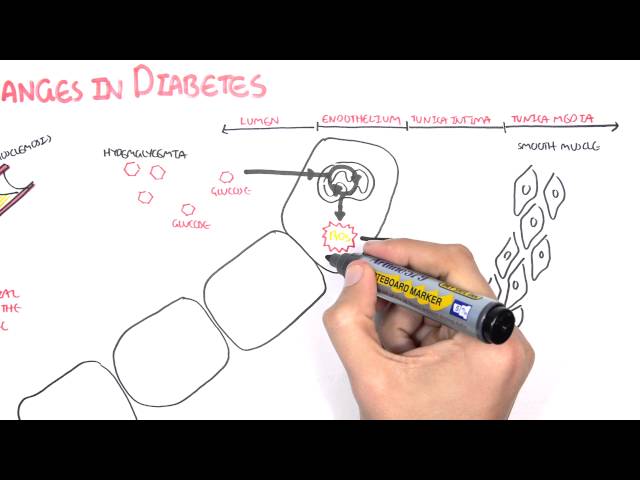
Diabetes and macrovascular complications refer to the development of large blood vessel diseases in individuals with diabetes. These complications can significantly impact the health and well-being of diabetic patients and are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality.
The presence of diabetes can accelerate the development and progression of macrovascular complications, including coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage the blood vessels over time, leading to the formation of plaques, narrowing of arteries, and impaired blood flow.
Understanding the relationship between diabetes and macrovascular complications is crucial for healthcare providers and individuals with diabetes. Early detection, management, and lifestyle modifications can help prevent or delay the onset of these complications, improving the overall health outcomes and quality of life for diabetic patients.
Diabetes and Macrovascular Complications
Understanding the various dimensions of diabetes and macrovascular complications is crucial for effective management and prevention. Here are eight key aspects to consider:
- Pathophysiology: High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels, leading to plaque formation and impaired blood flow.
- Risk Factors: Diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking increase the risk of macrovascular complications.
- Coronary Artery Disease: Reduced blood flow to the heart can cause chest pain, heart attack, and heart failure.
- Stroke: Blood clots or bleeding in the brain due to damaged blood vessels can lead to stroke.
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Narrowed arteries in the legs and feet can cause pain, numbness, and tissue damage.
- Prevention: Managing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, and quitting smoking can prevent or delay complications.
- Treatment: Medications, lifestyle changes, and procedures like angioplasty and stenting aim to improve blood flow and prevent further complications.
- Prognosis: Early detection and management can improve outcomes, but macrovascular complications remain a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients.
These aspects highlight the complex interplay between diabetes and macrovascular complications. By understanding these dimensions, healthcare providers and individuals with diabetes can work together to implement effective strategies for prevention, early detection, and management, ultimately improving the health and well-being of diabetic patients.
Pathophysiology
In the context of diabetes and macrovascular complications, understanding the pathophysiology is paramount. Elevated blood sugar levels, a hallmark of diabetes, exert a damaging effect on the blood vessels. Over time, this damage leads to the formation of plaque, a buildup of fatty substances, cholesterol, and other elements, within the arterial walls. As plaque accumulates, it narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of blood clots. This impaired blood flow can have severe consequences for various organs and tissues, potentially leading to complications such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
The connection between diabetes, high blood sugar levels, and impaired blood flow is a critical component in comprehending the development of macrovascular complications. By addressing these underlying factors through effective diabetes management, individuals can potentially mitigate the risks and improve their overall cardiovascular health.
In summary, the pathophysiology of high blood sugar levels damaging blood vessels serves as a foundation for understanding the mechanisms behind diabetes and macrovascular complications. Recognizing this connection empowers healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes to prioritize blood sugar control and implement preventive measures to safeguard against these debilitating complications.
Risk Factors
The link between risk factors such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking, and the development of macrovascular complications is well-established. These risk factors contribute to the underlying mechanisms that drive the progression of macrovascular complications in individuals with diabetes.
Diabetes, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, plays a central role in the development of macrovascular complications. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, leading to the formation of plaque, a buildup of fatty substances and cholesterol within the arterial walls. This plaque accumulation narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of blood clots.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, exerts additional stress on the blood vessel walls, further accelerating the damage caused by high blood sugar levels. Similarly, high cholesterol levels contribute to plaque formation, exacerbating the narrowing of arteries and increasing the risk of blockages. Smoking, on the other hand, damages the blood vessel lining, making it more susceptible to the formation of plaque and blood clots.
Understanding the connection between these risk factors and macrovascular complications is crucial for effective prevention and management strategies. By addressing and controlling these modifiable risk factors, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their chances of developing debilitating complications such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
In summary, the presence of diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking creates a synergistic effect that dramatically increases the risk of macrovascular complications. Recognizing and managing these risk factors are essential pillars in safeguarding the cardiovascular health of individuals with diabetes.
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a significant manifestation of macrovascular complications in individuals with diabetes. Reduced blood flow to the heart, a hallmark of CAD, can lead to a range of debilitating conditions, including chest pain (angina), heart attack (myocardial infarction), and heart failure.
- Atherosclerosis: Diabetes accelerates the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This plaque formation narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart and increasing the risk of CAD.
- Inflammation: Diabetes is associated with chronic inflammation, which contributes to the development and progression of CAD. Inflammatory markers are elevated in individuals with diabetes, promoting the formation of unstable plaques that are more likely to rupture and cause blood clots.
- Endothelial Dysfunction: Diabetes damages the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. This damage impairs the endothelium’s ability to regulate blood flow, promote vasodilation, and inhibit platelet aggregation, further increasing the risk of CAD.
- Hyperglycemia: Elevated blood sugar levels, a defining feature of diabetes, contribute to the development of CAD by promoting oxidative stress and inflammation. These processes damage the blood vessels and accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis.
The connection between CAD and diabetes and macrovascular complications underscores the critical need for effective diabetes management to prevent or delay the onset of these debilitating conditions. Early detection, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medical interventions are essential in safeguarding the cardiovascular health of individuals with diabetes.
Stroke
Stroke, a devastating complication of diabetes, occurs when blood clots block blood flow to the brain or when weakened blood vessels rupture, causing bleeding in the brain. Diabetes significantly increases the risk of stroke, and individuals with diabetes are more likely to experience recurrent strokes.
- Atherosclerosis: Diabetes accelerates the development of atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in arteries. Plaque formation narrows the arteries, including those supplying blood to the brain, increasing the risk of blood clots and stroke.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation, a hallmark of diabetes, contributes to stroke risk. Inflammatory markers are elevated in people with diabetes, promoting the formation of unstable plaques that are more likely to rupture and cause blood clots.
- Endothelial Dysfunction: Diabetes damages the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. This damage impairs the endothelium’s ability to regulate blood flow and promote vasodilation, contributing to stroke risk.
- Blood Sugar Control: Poor blood sugar control is associated with an increased risk of stroke. High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels, making them more susceptible to damage and rupture.
The connection between stroke and diabetes and macrovascular complications underscores the critical need for effective diabetes management to prevent or delay the onset of these debilitating conditions. Early detection, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medical interventions are essential in safeguarding the cardiovascular health of individuals with diabetes.
Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common complication of diabetes, affecting up to 20% of individuals with the condition. PAD occurs when arteries in the legs and feet become narrowed or blocked, restricting blood flow to these areas. This narrowing is often caused by atherosclerosis, a buildup of plaque in the arteries. Diabetes accelerates the development and progression of atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of PAD.
The reduced blood flow caused by PAD can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, and cramping in the legs and feet. In severe cases, PAD can cause tissue damage and ulceration, which can be difficult to treat and may lead to amputation.
PAD is a serious complication of diabetes and can significantly impact quality of life. It is important for individuals with diabetes to be aware of the risk factors for PAD and to take steps to prevent its development. These steps include managing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking. Early diagnosis and treatment of PAD are also important to prevent serious complications.
Prevention
In the context of diabetes and macrovascular complications, prevention is paramount. Managing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, and quitting smoking are cornerstone strategies to mitigate the risks and delay the onset of these debilitating conditions.
- Managing blood sugar levels: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels are a primary driver of macrovascular complications. Consistently high blood sugar damages blood vessels, leading to plaque buildup, inflammation, and impaired blood flow. Stringent glucose control through medication, diet, and exercise can significantly reduce the risk of developing these complications.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for diabetes and macrovascular complications. Excess weight puts strain on the heart and blood vessels, contributing to plaque formation and increasing the likelihood of blood clots. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity is crucial for reducing these risks.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking is one of the most detrimental habits for cardiovascular health. It damages the blood vessel lining, promotes inflammation, and increases the risk of blood clots. Quitting smoking is essential for individuals with diabetes to safeguard their vascular health.
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals with diabetes can proactively reduce their risk of developing macrovascular complications. These lifestyle modifications and behavioral changes empower individuals to take control of their health and improve their long-term outcomes.
Treatment
In the context of diabetes and macrovascular complications, effective treatment strategies are crucial to improve blood flow, prevent further complications, and enhance the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
- Medications: Antiplatelet agents, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, reduce the risk of blood clots and improve blood flow. Statins lower cholesterol levels, while ACE inhibitors and ARBs reduce blood pressure, all contributing to improved cardiovascular health.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is paramount. Quitting smoking and managing blood sugar levels are essential to reduce the risk of macrovascular complications.
- Angioplasty and stenting: These procedures aim to widen narrowed arteries and improve blood flow. Angioplasty involves inflating a balloon to widen the artery, while stenting involves placing a small mesh tube to keep the artery open.
These treatment options, when implemented in conjunction with regular monitoring and patient education, can significantly reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other life-threatening complications for individuals with diabetes.
Prognosis
Understanding the prognosis of macrovascular complications in diabetes is crucial for effective management and prevention strategies. Despite advancements in healthcare, macrovascular complications remain a significant cause of morbidity and mortality among diabetic patients.
- Early detection and management: Prompt identification and appropriate management of macrovascular complications can significantly improve patient outcomes. Regular screenings, such as blood pressure monitoring, lipid profiles, and foot examinations, are essential for early detection. Early intervention with lifestyle modifications, medications, or procedures can prevent or delay the progression of complications.
- Morbidity and mortality: Macrovascular complications contribute to substantial morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease can lead to severe disability, reduced quality of life, and even premature. Understanding the high-risk nature of these complications emphasizes the importance of effective diabetes management.
- Multifactorial causes: The development and progression of macrovascular complications in diabetes are influenced by various factors, including poorly controlled blood sugar levels, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and smoking. Addressing these modifiable risk factors through lifestyle changes and medications is essential for reducing the risk of complications.
- Patient education and empowerment: Educating diabetic patients about the risks, symptoms, and management of macrovascular complications is crucial for self-care and adherence to treatment plans. Empowering patients to monitor their health, make informed decisions, and seek timely medical attention can significantly improve outcomes.
In conclusion, the prognosis of macrovascular complications in diabetes highlights the importance of early detection, comprehensive management, and patient engagement. By understanding the multifaceted nature of these complications and implementing effective preventive measures, healthcare providers and diabetic patients can work together to improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
FAQs on Diabetes and Macrovascular Complications
This section addresses frequently asked questions about diabetes and its associated macrovascular complications to provide concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What are the common macrovascular complications associated with diabetes?
Diabetes can lead to various macrovascular complications, including coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. These conditions arise from damage to large blood vessels due to high blood sugar levels and other factors.
Question 2: How does diabetes contribute to macrovascular complications?
Elevated blood sugar levels damage the blood vessel lining, leading to inflammation and the formation of plaquea buildup of fatty substances and cholesterol. This plaque narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow and increasing the risk of blood clots and blockages.
Question 3: Who is at high risk for developing macrovascular complications from diabetes?
Individuals with poorly controlled blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and a history of smoking are at increased risk for macrovascular complications. Age and family history of cardiovascular disease can also be contributing factors.
Question 4: What are the symptoms of macrovascular complications?
Symptoms vary depending on the specific complication. Coronary artery disease may cause chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Stroke can manifest as sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, speech difficulties, and vision problems. Peripheral artery disease may lead to leg pain, cramping, and numbness.
Question 5: How can I prevent macrovascular complications if I have diabetes?
Effective diabetes management is crucial. Control blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, engage in regular physical activity, and quit smoking. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels is also essential.
Question 6: What treatments are available for macrovascular complications in diabetes?
Treatment options vary depending on the severity and type of complication. They may include medications to control blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar; lifestyle modifications; and procedures such as angioplasty or surgery to improve blood flow.
Summary:
Macrovascular complications are serious consequences of diabetes that can significantly impact health. Understanding the risks, symptoms, and preventive measures is crucial for diabetic individuals. Effective diabetes management, regular monitoring, and timely treatment can help prevent or delay the onset and progression of these complications, improving the overall health and well-being of diabetic patients.
Transition to the next article section:
For further information and support, consult your healthcare provider or reputable medical organizations specializing in diabetes care.
Tips for Managing Diabetes and Macrovascular Complications
Effectively managing diabetes and preventing its associated macrovascular complications requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some essential tips to guide individuals with diabetes:
Tip 1: Maintain Optimal Blood Sugar Control
Consistently monitoring and managing blood sugar levels is paramount. Adherence to prescribed medications, a balanced diet, and regular physical activity are crucial in maintaining glycemic control and reducing the risk of macrovascular complications.
Tip 2: Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
High blood pressure and cholesterol levels contribute to the development and progression of macrovascular complications. Regular monitoring and appropriate medical interventions, including medications and lifestyle modifications, are essential for managing these risk factors effectively.
Tip 3: Quit Smoking
Smoking cessation is a critical step in reducing the risk of macrovascular complications. Smoking damages blood vessels and increases inflammation, exacerbating the negative effects of diabetes on the cardiovascular system.
Tip 4: Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity helps improve blood sugar control, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce blood pressure. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Tip 5: Maintain a Healthy Diet
A balanced and nutritious diet is essential for managing diabetes and preventing macrovascular complications. Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats, while limiting sugary drinks, processed foods, and excessive sodium intake.
Tip 6: Get Regular Checkups and Screenings
Regular checkups and screenings are crucial for early detection and intervention of macrovascular complications. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate screening schedule based on your individual risk factors.
Tip 7: Take Medications as Prescribed
Adhering to prescribed medications, such as blood sugar-lowering agents, antiplatelet drugs, or blood pressure medications, is essential for effectively managing diabetes and reducing the risk of macrovascular complications.
Tip 8: Educate Yourself and Others
Empower yourself with knowledge about diabetes and its complications. Stay informed about the latest advancements in diabetes management and share accurate information with family and friends to promote a better understanding of the condition.
Summary:
By implementing these tips, individuals with diabetes can proactively reduce their risk of developing macrovascular complications and improve their overall health outcomes. Remember, effective diabetes management is a collaborative effort between healthcare providers and individuals with diabetes, and open communication and shared decision-making are essential for achieving optimal results.
Transition to the conclusion:
Managing diabetes and preventing macrovascular complications requires commitment and a holistic approach. These tips provide a solid foundation for individuals to take an active role in their health and well-being.
Conclusion
Diabetes and macrovascular complications pose significant challenges to individuals and healthcare systems alike. This article has explored the intricate relationship between diabetes, elevated blood sugar levels, and the development of macrovascular complications, including coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. We have emphasized the importance of early detection, comprehensive management, and patient engagement in preventing or delaying the onset and progression of these debilitating conditions.
Effective management of diabetes and its associated macrovascular complications requires a multifaceted approach. Maintaining optimal blood sugar control, managing blood pressure and cholesterol, quitting smoking, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, getting regular checkups and screenings, taking medications as prescribed, and educating oneself and others are all essential aspects of reducing the risk and improving outcomes for individuals with diabetes. By implementing these measures, individuals can proactively safeguard their cardiovascular health and enhance their overall well-being.
Youtube Video: