Within the realm of healthcare, “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers” pertains to a specific section or guideline within a larger document or protocol addressing diabetic emergencies. It signifies the presence of two distinct and critical answers or instructions related to managing such emergencies effectively. These answers are crucial for healthcare professionals to promptly identify and respond to life-threatening situations involving individuals with diabetes.
Diabetic emergencies encompass a spectrum of severe and potentially life-threatening conditions, including diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hypoglycemia. Timely recognition and appropriate management of these emergencies are essential to prevent severe complications or even fatalities. The “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers” provide concise and essential guidance to healthcare providers on the appropriate steps to take when encountering such emergencies.
Understanding and adhering to these emergency answers empower healthcare professionals to deliver prompt and effective care, potentially saving lives and improving patient outcomes. As we delve into the main article, we will explore the significance of these answers in greater detail, examining their role in the overall management of diabetic emergencies and highlighting strategies for their effective implementation in clinical practice.
2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers
In the realm of diabetic emergencies, timely recognition and appropriate management are paramount. The “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers” provide concise guidance for healthcare professionals in such situations. These answers encompass various key aspects, each playing a crucial role in ensuring effective emergency care for diabetic patients.
- Identification: Recognizing the signs and symptoms of diabetic emergencies.
- Assessment: Evaluating the patient’s condition and determining the appropriate course of action.
- Intervention: Administering necessary medications and treatments to stabilize the patient’s condition.
- Monitoring: Closely observing the patient’s response to treatment and making necessary adjustments.
- Communication: Relaying critical information to other healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care.
- Documentation: Accurately recording the patient’s condition, treatment provided, and response to care.
- Education: Providing guidance and support to patients and their families on managing diabetic emergencies.
These key aspects are interconnected and equally important in ensuring optimal patient outcomes. For instance, accurate identification of diabetic emergencies allows for prompt assessment and intervention, potentially saving lives. Effective monitoring enables timely adjustments to treatment, while clear communication ensures continuity of care. Proper documentation serves as a valuable record for future reference and quality improvement initiatives. Moreover, patient education empowers individuals to recognize and manage potential emergencies, reducing the risk of complications.
Identification
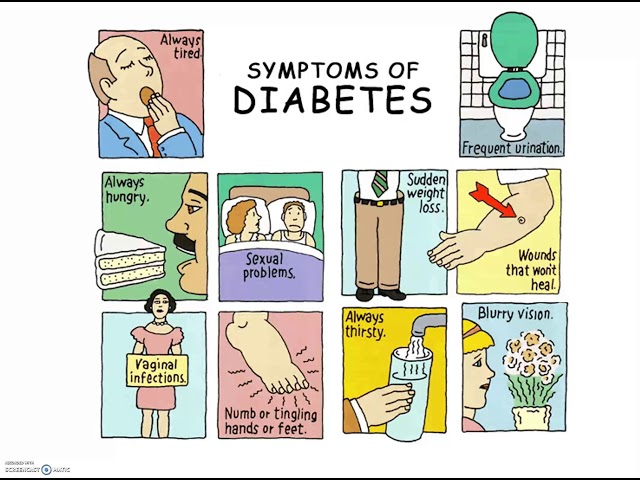
In the context of “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers,” identification serves as the cornerstone for effective emergency management. It involves recognizing the distinctive signs and symptoms associated with diabetic emergencies, such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hypoglycemia, which can vary depending on the individual and the specific condition. Prompt identification is essential because it triggers the subsequent steps in the emergency response protocol, ensuring timely intervention and potentially life-saving care.
Consider the example of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Early identification of symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, and fruity-smelling breath is crucial. Delay in recognizing these signs can lead to severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and potentially fatal complications. By contrast, early identification allows for prompt administration of intravenous fluids, insulin, and other necessary treatments, significantly improving the chances of a positive outcome.
The practical significance of accurate identification extends beyond individual patient care. It also contributes to broader public health efforts aimed at preventing and managing diabetic emergencies. By educating individuals with diabetes and the general population about the signs and symptoms of these emergencies, we can empower them to seek timely medical attention, reducing the risk of severe complications and enhancing overall health outcomes.
Assessment
Within the context of “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers,” assessment plays a pivotal role in ensuring effective emergency management. It involves evaluating the patient’s condition meticulously to determine the most appropriate course of action, considering factors such as the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and vital signs. Accurate assessment is crucial because it directly influences the subsequent steps in the emergency response protocol, guiding treatment decisions and potentially saving lives.
-
Triage
In emergency situations, triage is a critical component of assessment. It involves rapidly assessing and prioritizing patients based on the severity of their condition to ensure that those with the most urgent needs receive immediate attention. In the context of diabetic emergencies, triage helps identify patients who require immediate stabilization and treatment, such as those with severe hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis.
-
Diagnostic testing
Diagnostic testing plays a vital role in assessment, particularly when the patient’s symptoms are ambiguous or non-specific. Blood glucose monitoring, urine ketones testing, and arterial blood gas analysis are commonly used to confirm or rule out diabetic emergencies and guide treatment decisions.
-
Physical examination
Physical examination is essential for assessing the patient’s overall condition and identifying any potential complications. It involves checking vital signs, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate, as well as examining the patient’s skin, mucous membranes, and neurological status.
-
Medical history review
Reviewing the patient’s medical history provides valuable insights into their overall health status, previous episodes of diabetic emergencies, and any co-existing medical conditions. This information helps guide the assessment process and tailor treatment decisions to the individual patient’s needs.
These facets of assessment are interconnected and collectively contribute to the effective management of diabetic emergencies. By accurately assessing the patient’s condition and determining the appropriate course of action, healthcare professionals can optimize treatment outcomes and improve patient safety.
Intervention
Within the context of “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers,” intervention serves as the cornerstone of effective emergency management. It involves administering necessary medications and treatments to stabilize the patient’s condition, potentially saving lives and preventing severe complications. The importance of intervention cannot be overstated, as it directly influences the patient’s immediate and long-term prognosis.
Consider the example of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Prompt intervention with intravenous fluids and insulin is crucial in correcting the severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalances that characterize this condition. Delay in treatment can lead to further complications, such as cerebral edema, which can be life-threatening. Conversely, timely intervention can restore the patient’s fluid and electrolyte balance, preventing these complications and improving the chances of a positive outcome.
The practical significance of effective intervention extends beyond individual patient care. It also contributes to broader public health efforts aimed at reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with diabetic emergencies. By equipping healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills to administer necessary medications and treatments, we can improve the overall quality of care for patients with diabetes and reduce the risk of severe complications.
Monitoring
In the context of “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers,” monitoring plays a critical role in ensuring effective emergency management. It involves closely observing the patient’s response to treatment and making necessary adjustments to ensure optimal outcomes.
-
Tracking vital signs
Monitoring vital signs, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate, provides valuable insights into the patient’s overall condition and response to treatment. Significant deviations from normal ranges may indicate the need for adjustments in treatment or further investigation.
-
Assessing blood glucose levels
In diabetic emergencies, such as hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis, monitoring blood glucose levels is essential. Regular testing helps guide insulin administration, fluid resuscitation, and other treatments to maintain stable glucose levels.
-
Observing for complications
Close monitoring allows healthcare professionals to identify and address potential complications early on. For instance, in diabetic ketoacidosis, monitoring for signs of cerebral edema or electrolyte imbalances is crucial to prevent severe neurological consequences.
-
Adjusting treatment plans
Based on the patient’s response to treatment, adjustments may be necessary to optimize outcomes. For example, if a patient’s blood glucose levels are not responding as expected, the insulin dosage or infusion rate may need to be adjusted.
Effective monitoring is essential for ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate and timely care during diabetic emergencies. By closely observing the patient’s response to treatment and making necessary adjustments, healthcare professionals can improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Communication
Within the context of “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers,” communication plays a vital role in ensuring effective emergency management. It involves relaying critical information to other healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care, such as physicians, nurses, and specialists, to facilitate coordinated and timely decision-making.
-
Providing patient updates
Effective communication ensures that all healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care have up-to-date information about the patient’s condition, treatment plan, and response to treatment. This enables them to make informed decisions and provide seamless care.
-
Consulting with specialists
In complex diabetic emergencies, consultation with specialists may be necessary. Effective communication facilitates timely referrals and efficient transfer of patient information, ensuring that the patient receives the most appropriate care.
-
Coordinating care transitions
When patients are transferred between different care settings, such as from the emergency department to the intensive care unit or a specialized diabetes center, effective communication ensures a smooth transition of care. It involves providing detailed patient information, including medical history, current condition, and treatment plan.
-
Documenting patient information
Accurate and timely documentation of the patient’s condition, treatment, and response to care is crucial for effective communication. It serves as a reliable source of information for all healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care, facilitating continuity of care and reducing the risk of errors.
Effective communication among healthcare professionals is essential for ensuring that patients with diabetic emergencies receive the best possible care. By relaying critical information accurately and efficiently, healthcare professionals can improve patient outcomes, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance the overall quality of care.
Documentation
Within the context of “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers,” documentation plays a critical role in ensuring effective emergency management. It involves accurately recording the patient’s condition, treatment provided, and response to care, providing a reliable and detailed account of the patient’s journey through the emergency.
-
Establishing a clear baseline
Accurate documentation establishes a clear baseline of the patient’s condition upon presentation to the emergency department. This includes recording vital signs, physical examination findings, and relevant medical history. It provides a benchmark against which subsequent changes can be compared, enabling healthcare professionals to track the patient’s progress and response to treatment.
-
Facilitating effective communication
Comprehensive documentation facilitates effective communication among healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care. It ensures that all members of the team have access to the same up-to-date information, reducing the risk of miscommunication and errors. Clear documentation also supports seamless transitions of care between different settings, such as from the emergency department to the intensive care unit or a specialized diabetes center.
-
Supporting decision-making
Accurate documentation supports informed decision-making throughout the emergency management process. By providing a detailed record of the patient’s condition and response to treatment, healthcare professionals can make more informed decisions about the patient’s care plan, including the selection of appropriate medications, interventions, and monitoring strategies.
-
Enabling quality improvement
High-quality documentation is essential for quality improvement initiatives. It allows healthcare professionals to retrospectively review cases, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to enhance the quality of care provided to patients with diabetic emergencies.
In conclusion, documentation is an integral part of “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers.” Accurate and comprehensive documentation ensures effective communication, supports informed decision-making, and facilitates quality improvement, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes and enhanced emergency care for diabetic patients.
Education
Education plays a crucial role within the framework of “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers” by empowering patients and their families with the knowledge and skills necessary to manage diabetic emergencies effectively. This educational component is not merely an isolated aspect but an integral part of ensuring optimal patient outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
By providing clear guidance and support, healthcare professionals equip patients and their families with the confidence and ability to recognize the signs and symptoms of diabetic emergencies, such as hypoglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis. This understanding empowers them to take prompt action, such as administering glucagon or seeking immediate medical attention, which can be life-saving. Moreover, education empowers patients to make informed decisions about their diabetes management, including medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and self-monitoring techniques, which can help prevent emergencies from occurring in the first place.
The practical significance of patient education extends beyond individual well-being. It contributes to reducing the overall burden of diabetic emergencies on healthcare systems. By equipping patients with the knowledge and skills to manage their condition effectively, the number of emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and long-term complications can be reduced. This not only improves the quality of life for patients and their families but also optimizes resource allocation within healthcare systems.
In conclusion, the educational component of “2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers” is not simply an add-on but an essential pillar in the management of diabetic emergencies. By empowering patients and their families with the knowledge and skills to recognize, respond to, and prevent emergencies, we enhance patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and ultimately improve the well-being of individuals living with diabetes.
FAQs on Diabetic Emergencies
Diabetic emergencies are serious medical conditions that require prompt recognition and appropriate management. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about diabetic emergencies, providing essential information for individuals with diabetes and their caregivers:
Question 1: What are the common types of diabetic emergencies?
Answer: The two most common types of diabetic emergencies are hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious condition characterized by high blood sugar, ketones in the urine, and dehydration.
Question 2: What are the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia?
Answer: Symptoms of hypoglycemia include sweating, shakiness, hunger, confusion, and rapid heartbeat. If left untreated, severe hypoglycemia can lead to seizures, coma, or even death.
Question 3: What should I do if someone is experiencing hypoglycemia?
Answer: If you suspect someone is experiencing hypoglycemia, give them a sugary drink or food immediately. If the person is unconscious, glucagon should be administered.
Question 4: What are the signs and symptoms of DKA?
Answer: Symptoms of DKA include excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, vomiting, and fruity-smelling breath. DKA is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
Question 5: What should I do if someone is experiencing DKA?
Answer: If you suspect someone is experiencing DKA, call for emergency medical assistance immediately. Do not attempt to treat DKA at home.
Question 6: How can I prevent diabetic emergencies?
Answer: The best way to prevent diabetic emergencies is to manage your blood sugar levels effectively through medication, diet, and exercise. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and adherence to your treatment plan are crucial.
Remember, diabetic emergencies are serious medical conditions that require prompt recognition and appropriate management. By understanding the common types of emergencies, their signs and symptoms, and the necessary steps to take, you can help ensure the safety and well-being of individuals with diabetes.
For more in-depth information and guidance on diabetic emergencies, consult with your healthcare provider or refer to reputable medical resources.
Tips for Managing Diabetic Emergencies
Diabetic emergencies are serious medical conditions that require prompt recognition and appropriate management. Here are some essential tips to help you respond effectively to diabetic emergencies:
Tip 1: Learn the Signs and Symptoms
Familiarize yourself with the common signs and symptoms of diabetic emergencies, such as hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). This knowledge will enable you to recognize emergencies early on and seek medical attention promptly.
Tip 2: Keep a Glucagon Kit Handy
Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels. Keep a glucagon kit readily available in case of a hypoglycemic emergency. Follow the instructions carefully and administer glucagon as directed.
Tip 3: Carry Medical Identification
Wear a medical ID bracelet or necklace that clearly states you have diabetes. This information can be lifesaving in an emergency situation where you are unable to communicate.
Tip 4: Educate Your Loved Ones
Inform your family, friends, and colleagues about diabetes and the signs and symptoms of diabetic emergencies. Educate them on how to recognize and respond to these emergencies, including when to call for medical help.
Tip 5: Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing emergencies. Check your blood sugar levels as directed by your healthcare provider and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Tip 6: Follow Your Treatment Plan
Adhering to your prescribed treatment plan, including medication, diet, and exercise, is essential for managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of emergencies.
Tip 7: Seek Medical Attention Promptly
Do not hesitate to seek medical attention if you experience any signs or symptoms of a diabetic emergency. Early intervention can prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
Summary:
By following these tips and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can enhance your ability to manage diabetic emergencies effectively. Remember, knowledge, preparedness, and timely action can make a significant difference in the outcome of a diabetic emergency.
Conclusion
“2.3 2 diabetic emergency answers” encapsulates critical guidance within a comprehensive emergency management framework for diabetic emergencies. This concise yet comprehensive resource empowers healthcare professionals with essential knowledge and protocols for the timely recognition, assessment, intervention, and management of these life-threatening conditions.
Understanding and adhering to these emergency answers are not merely healthcare imperatives but ethical obligations. By equipping ourselves with this knowledge, we enhance our ability to respond effectively, potentially saving lives and improving patient outcomes. As we continue to explore advancements in diabetes management, the significance of these emergency answers remains paramount in ensuring the well-being of individuals living with this condition.
Youtube Video: