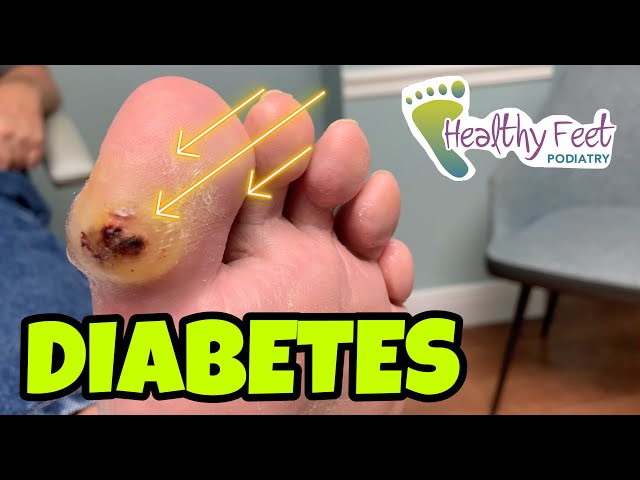
Diabetes blisters, also known as bullosis diabeticorum, are fluid-filled blisters that develop on the skin of people with diabetes. They are caused by damage to the small blood vessels in the skin, which can lead to leakage of fluid and the formation of blisters. Diabetes blisters are typically found on the feet, hands, and legs, and they can range in size from small to large. They are often painful and can become infected if they are not treated properly.
Diabetes blisters are a serious complication of diabetes, and they can lead to a number of health problems, including:
- Infection
- Ulcers
- Gangrene
- Amputation
People with diabetes should be aware of the symptoms of diabetes blisters and seek medical attention if they develop any. Early treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Diabetes Blister
Diabetes blisters, also known as bullosis diabeticorum, are fluid-filled blisters that develop on the skin of people with diabetes. They are caused by damage to the small blood vessels in the skin, which can lead to leakage of fluid and the formation of blisters. Diabetes blisters are typically found on the feet, hands, and legs, and they can range in size from small to large. They are often painful and can become infected if they are not treated properly.
- Cause: Diabetes
- Location: Feet, hands, and legs
- Size: Small to large
- Symptoms: Pain, itching, burning
- Complications: Infection, ulcers, gangrene, amputation
- Treatment: Antibiotics, wound care, surgery
- Prevention: Good blood sugar control, proper foot care
- Outlook: With proper treatment, diabetes blisters can usually be healed without complications.
Diabetes blisters are a serious complication of diabetes, and they can lead to a number of health problems. It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of diabetes blisters and to seek medical attention if they develop any. Early treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Cause
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells. Without insulin, glucose builds up in the blood and can damage the blood vessels and nerves.
Damage to the blood vessels in the skin can lead to leakage of fluid and the formation of diabetes blisters. Diabetes blisters are typically found on the feet, hands, and legs, and they can range in size from small to large. They are often painful and can become infected if they are not treated properly.
Diabetes blisters are a serious complication of diabetes, and they can lead to a number of health problems, including infection, ulcers, gangrene, and amputation. People with diabetes should be aware of the symptoms of diabetes blisters and seek medical attention if they develop any. Early treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Location
Diabetes blisters are typically found on the feet, hands, and legs because these areas are more likely to experience friction and pressure. Friction can occur when the skin rubs against clothing or shoes, while pressure can occur when the skin is pressed against a hard surface. Both friction and pressure can damage the blood vessels in the skin and lead to the formation of blisters.
- Feet: The feet are the most common location for diabetes blisters because they are constantlying friction and pressure from walking and standing. Diabetes blisters on the feet can be very painful and can make it difficult to walk.
- Hands: The hands are another common location for diabetes blisters because they are often used to perform tasks that involve friction and pressure, such as gripping objects or typing. Diabetes blisters on the hands can be painful and can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
- Legs: The legs are less common location for diabetes blisters than the feet and hands, but they can still occur. Diabetes blisters on the legs can be caused by friction from clothing or pressure from sitting or lying down in one position for too long.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of diabetes blisters and to seek medical attention if they develop any. Early treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Size
The size of a diabetes blister can vary from small to large. Small blisters are typically less than 1 centimeter in diameter, while large blisters can be several centimeters in diameter. The size of a diabetes blister is not necessarily indicative of its severity, but it can be a factor in determining the best course of treatment.
Small diabetes blisters can often be treated with simple home care, such as keeping the area clean and dry and applying a bandage. Large diabetes blisters may require more aggressive treatment, such as draining the fluid and applying antibiotics. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a large diabetes blister.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of diabetes blisters and to seek medical attention if they develop any. Early treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Symptoms
Diabetes blisters are often painful, itchy, and burning. These symptoms can be caused by a number of factors:
- Nerve damage: Diabetes can damage the nerves in the skin, which can lead to pain, numbness, and tingling. These symptoms can also make it difficult to feel blisters and other injuries, which can lead to further problems.
- Inflammation: Diabetes can also cause inflammation in the skin, which can lead to pain, swelling, and redness.
- Infection: Diabetes blisters can become infected, which can lead to pain, swelling, redness, and drainage.
- Pressure: Diabetes blisters can be painful when they are pressed on. This is especially true if the blisters are on the feet and are subjected to pressure from walking or standing.
The pain, itching, and burning of diabetes blisters can be very uncomfortable and can interfere with everyday activities. It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of these symptoms and to seek medical attention if they develop any blisters.
Complications
Diabetes blisters can lead to a number of serious complications, including infection, ulcers, gangrene, and amputation. These complications are caused by the damage to the blood vessels and nerves that occurs in diabetes. This damage can lead to a number of problems, including:
- Infection: Diabetes blisters can become infected if they are not treated properly. This can lead to pain, swelling, redness, and drainage. In some cases, the infection can spread to the bone or other parts of the body.
- Ulcers: Diabetes blisters can also lead to ulcers. Ulcers are open sores that can develop on the skin, bones, or muscles. They are often painful and can be difficult to heal.
- Gangrene: Gangrene is a serious infection that can occur when the blood supply to a part of the body is cut off. This can happen if diabetes blisters become infected and the infection spreads to the surrounding tissue. Gangrene can lead to the loss of a limb or even death.
- Amputation: In some cases, diabetes blisters can lead to amputation. This is the surgical removal of a limb or part of a limb. Amputation is usually only necessary if the infection or gangrene has become severe.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of diabetes blisters and to seek medical attention if they develop any. Early treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Treatment
Diabetes blisters require prompt and appropriate treatment to prevent complications such as infection, ulcers, gangrene, and amputation. Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics, wound care, and in some cases, surgery.
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used to treat or prevent infections in diabetes blisters. They may be taken orally or applied topically to the affected area. Common antibiotics used for diabetes blisters include amoxicillin-clavulanate, cephalexin, and ciprofloxacin.
Wound care: Proper wound care is essential for preventing infection and promoting healing of diabetes blisters. This involves keeping the wound clean and dry, applying dressings to protect the wound from further injury, and monitoring the wound for signs of infection.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a diabetes blister or to treat complications such as infection or gangrene. Surgery may also be necessary to relieve pressure on a blister that is causing pain or discomfort.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of diabetes blisters and to seek medical attention if they develop any. Early treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Prevention
Diabetes blisters are a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to infection, ulcers, gangrene, and amputation. Fortunately, there are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent diabetes blisters, including good blood sugar control and proper foot care.
-
Good blood sugar control
Good blood sugar control is essential for preventing diabetes blisters. When blood sugar levels are high, it can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the skin, which can lead to the formation of blisters. People with diabetes should work with their doctor to develop a treatment plan that will help them to keep their blood sugar levels under control.
-
Proper foot care
Proper foot care is also important for preventing diabetes blisters. People with diabetes should inspect their feet daily for any signs of blisters, cuts, or other injuries. They should also wear comfortable shoes that fit well and protect their feet from injury. Additionally, people with diabetes should avoid walking barefoot and should keep their feet clean and dry.
By following these tips, people with diabetes can help to prevent diabetes blisters and other serious foot complications.
Outlook
Diabetes blisters are a common complication of diabetes, but they can usually be healed without complications with proper treatment. This is because the blisters are caused by damage to the small blood vessels in the skin, and this damage can be repaired with proper medical care.
- Early treatment is key. The sooner diabetes blisters are treated, the less likely they are to become infected or develop other complications.
- Proper wound care is essential. This includes keeping the blisters clean and dry, and applying antibiotic ointment to prevent infection.
- In some cases, antibiotics may be necessary. This is typically the case if the blisters become infected.
- Surgery may be necessary in rare cases. This is typically only necessary if the blisters are very large or if they become infected and do not respond to antibiotics.
By following these tips, people with diabetes can help to ensure that their diabetes blisters heal quickly and without complications.
Diabetes Blister FAQs
Diabetes blisters are a common complication of diabetes, and they can be a cause of significant pain and discomfort. Here are some frequently asked questions about diabetes blisters:
Question 1: What causes diabetes blisters?
Diabetes blisters are caused by damage to the small blood vessels in the skin. This damage can be caused by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to the formation of blisters.
Question 2: Where do diabetes blisters typically occur?
Diabetes blisters can occur anywhere on the body, but they are most common on the feet, hands, and legs.
Question 3: Are diabetes blisters painful?
Yes, diabetes blisters can be painful. The pain can range from mild to severe, and it can be worse if the blisters become infected.
Question 4: How are diabetes blisters treated?
Diabetes blisters are typically treated with antibiotics to prevent infection, wound care to keep the blisters clean and dry, and pain relievers to reduce discomfort. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a diabetes blister.
Question 5: Can diabetes blisters be prevented?
Yes, there are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent diabetes blisters, including keeping their blood sugar levels under control, wearing comfortable shoes, and inspecting their feet daily for any signs of blisters or other injuries.
Question 6: What is the outlook for people with diabetes blisters?
With proper treatment, diabetes blisters can usually be healed without complications. However, it is important to seek medical attention if you have diabetes blisters, as they can become infected and lead to serious complications.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
Diabetes blisters are a common complication of diabetes, but they can be prevented and treated. If you have diabetes, it is important to keep your blood sugar levels under control, wear comfortable shoes, and inspect your feet daily for any signs of blisters or other injuries.
Transition to the next article section:
For more information on diabetes blisters, please visit our website or talk to your doctor.
Tips for Preventing and Treating Diabetes Blisters
Diabetes blisters are a common complication of diabetes, but they can be prevented and treated with proper care. Here are five tips for preventing and treating diabetes blisters:
Tip 1: Keep your blood sugar levels under control.
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the skin, which can lead to the formation of blisters. People with diabetes should work with their doctor to develop a treatment plan that will help them to keep their blood sugar levels under control.Tip 2: Wear comfortable shoes.
Shoes that are too tight or too loose can put pressure on the feet and cause blisters. People with diabetes should wear comfortable shoes that fit well and protect their feet from injury.Tip 3: Inspect your feet daily.
People with diabetes should inspect their feet daily for any signs of blisters, cuts, or other injuries. This will help to catch any problems early and prevent them from becoming more serious.Tip 4: Treat blisters promptly.
If you develop a diabetes blister, it is important to treat it promptly to prevent infection. Clean the blister with soap and water and apply an antibiotic ointment. You may also need to take oral antibiotics if the blister becomes infected.Tip 5: See your doctor if you have any concerns.
If you have any concerns about diabetes blisters, see your doctor. They can help you to develop a treatment plan and prevent serious complications.Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By following these tips, people with diabetes can help to prevent and treat diabetes blisters. This will help to keep their feet healthy and prevent serious complications.Transition to the article’s conclusion:
If you have diabetes, it is important to take care of your feet and prevent blisters. By following these tips, you can help to keep your feet healthy and avoid serious complications.
Conclusion
Diabetes blisters are a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to infection, ulcers, gangrene, and amputation. However, with proper prevention and treatment, diabetes blisters can usually be healed without complications. People with diabetes should be aware of the symptoms of diabetes blisters and seek medical attention if they develop any. By following the tips outlined in this article, people with diabetes can help to prevent and treat diabetes blisters and keep their feet healthy.
Diabetes blisters are a reminder of the importance of good diabetes management. By keeping blood sugar levels under control, wearing comfortable shoes, and inspecting feet daily, people with diabetes can help to prevent blisters and other serious foot complications.
Youtube Video: