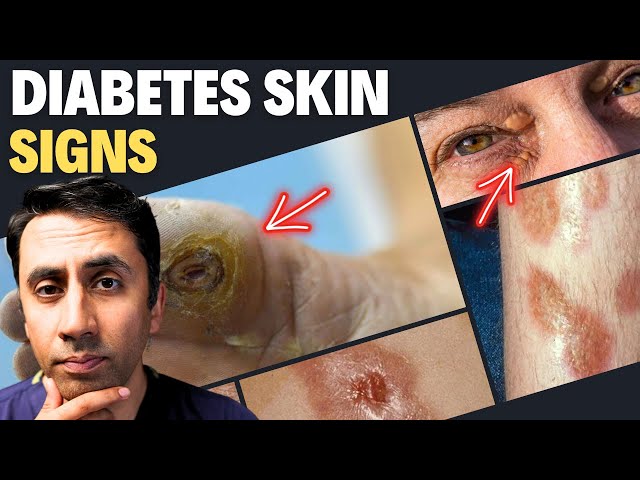
Diabetes infection is an infection that occurs in people with diabetes. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, and can affect any part of the body. Diabetes infection is a serious complication of diabetes and can lead to hospitalization and even death.
People with diabetes are more likely to develop infections because their immune system is weakened. This is due to the high levels of sugar in the blood, which can damage the white blood cells that fight infection. In addition, people with diabetes often have poor circulation, which can make it difficult for the immune system to reach infected areas.
The most common type of diabetes infection is a skin infection. This can be caused by bacteria that enter the skin through a cut or scrape. Skin infections in people with diabetes can be difficult to treat and may require antibiotics. Other types of diabetes infection include pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis.
Preventing diabetes infection is important for people with diabetes. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, taking antibiotics as prescribed, and practicing good hygiene. If you have diabetes, it is important to see your doctor regularly for checkups and to report any signs of infection.
diabetes infection
Diabetes infection is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to hospitalization and even death. There are several key aspects to consider when discussing diabetes infection:
- Cause: Diabetes infection can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
- Risk factors: People with diabetes are more likely to develop infections due to their weakened immune system and poor circulation.
- Types: The most common type of diabetes infection is a skin infection, but other types include pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of diabetes infection can vary depending on the type of infection, but may include fever, chills, pain, swelling, and redness.
- Treatment: Treatment for diabetes infection typically involves antibiotics or other medications, and may also require hospitalization.
- Prevention: Preventing diabetes infection is important for people with diabetes. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, taking antibiotics as prescribed, and practicing good hygiene.
These key aspects provide a comprehensive overview of diabetes infection, from its causes and risk factors to its symptoms, treatment, and prevention. Understanding these aspects is essential for people with diabetes and their healthcare providers in order to prevent and manage this serious complication.
Cause
Diabetes infection is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to hospitalization and even death. Understanding the cause of diabetes infection is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
There are several ways that bacteria, viruses, or fungi can cause diabetes infection. Bacteria can enter the body through a cut or scrape in the skin, or through the respiratory tract. Viruses can be spread through contact with an infected person or by inhaling airborne droplets. Fungi can enter the body through the skin or through the respiratory tract.
Once inside the body, bacteria, viruses, or fungi can cause infection by multiplying and damaging cells. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, including fever, chills, pain, swelling, and redness. In severe cases, diabetes infection can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition that occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream.
Understanding the cause of diabetes infection is important for several reasons. First, it helps us to develop effective prevention strategies. For example, we know that keeping blood sugar levels under control can help to prevent diabetes infection. Second, it helps us to choose the right treatment for diabetes infection. For example, if the infection is caused by bacteria, we will need to prescribe antibiotics. Third, it helps us to educate people with diabetes about the importance of preventing and treating infection.
In conclusion, the cause of diabetes infection is an important aspect of this serious complication. By understanding the cause of diabetes infection, we can develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Risk factors
Diabetes infection is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to hospitalization and even death. People with diabetes are more likely to develop infections because their immune system is weakened and their circulation is poor. These risk factors are closely connected to diabetes infection and play a significant role in its development and progression.
- Weakened immune system: Diabetes can damage the white blood cells that fight infection. This makes people with diabetes more susceptible to infections of all kinds, including skin infections, pneumonia, and urinary tract infections.
- Poor circulation: Diabetes can also damage the blood vessels, which can lead to poor circulation. This can make it difficult for the immune system to reach infected areas and fight the infection.
The connection between these risk factors and diabetes infection is clear. People with diabetes are more likely to develop infections because their immune system is weakened and their circulation is poor. These factors create a perfect storm for infection, making it more likely to occur and more difficult to treat.
Understanding the connection between these risk factors and diabetes infection is important for several reasons. First, it helps us to develop effective prevention strategies. For example, we know that keeping blood sugar levels under control can help to prevent diabetes infection. Second, it helps us to choose the right treatment for diabetes infection. For example, if the infection is caused by bacteria, we will need to prescribe antibiotics. Third, it helps us to educate people with diabetes about the importance of preventing and treating infection.
In conclusion, the risk factors of a weakened immune system and poor circulation are closely connected to diabetes infection. By understanding this connection, we can develop effective prevention and treatment strategies and empower people with diabetes to take control of their health.
Types
Diabetes infection is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to hospitalization and even death. Understanding the different types of diabetes infection is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
The most common type of diabetes infection is a skin infection. This can be caused by bacteria that enter the skin through a cut or scrape. Skin infections in people with diabetes can be difficult to treat and may require antibiotics. Other types of diabetes infection include:
- Pneumonia: This is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): These are infections of the urinary system that can be caused by bacteria.
- Sepsis: This is a life-threatening condition that occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream.
The connection between the different types of diabetes infection and diabetes infection as a whole is clear. All of these infections are more likely to occur in people with diabetes because their immune system is weakened and their circulation is poor. This makes it easier for bacteria, viruses, and fungi to enter the body and cause infection.
Understanding the different types of diabetes infection is important for several reasons. First, it helps us to develop effective prevention strategies. For example, we know that keeping blood sugar levels under control can help to prevent all types of diabetes infection. Second, it helps us to choose the right treatment for diabetes infection. For example, if the infection is caused by bacteria, we will need to prescribe antibiotics. Third, it helps us to educate people with diabetes about the importance of preventing and treating infection.
In conclusion, the different types of diabetes infection are closely connected to diabetes infection as a whole. By understanding the different types of diabetes infection, we can develop effective prevention and treatment strategies and empower people with diabetes to take control of their health.
Symptoms
The symptoms of diabetes infection can vary depending on the type of infection. However, there are some general symptoms that are common to most types of diabetes infection. These include:
- Fever: A fever is a body temperature that is higher than normal. Fever is a common symptom of infection, and it can be a sign that the body is fighting an infection.
- Chills: Chills are a feeling of coldness that can be accompanied by shivering. Chills are often a sign that the body is trying to raise its temperature to fight an infection.
- Pain: Pain is a common symptom of diabetes infection. The pain may be localized to the area of the infection, or it may be more widespread.
- Swelling: Swelling is another common symptom of diabetes infection. The swelling may be caused by inflammation or by a buildup of fluid in the tissues.
- Redness: Redness is a common symptom of diabetes infection. The redness may be caused by inflammation or by an increase in blood flow to the area of the infection.
The symptoms of diabetes infection can range from mild to severe. If you have any of the symptoms of diabetes infection, it is important to see your doctor right away.
Treatment
Treatment for diabetes infection is essential to prevent serious complications and improve the chances of a full recovery. The type of treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and the underlying cause. In some cases, antibiotics or other medications may be prescribed. In more severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections. They work by killing or stopping the growth of bacteria. Antibiotics are typically prescribed for skin infections, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia.
- Other medications: Other medications may be prescribed to treat diabetes infection. These medications may include antifungal medications, antiviral medications, or pain relievers.
- Hospitalization: Hospitalization may be necessary for severe diabetes infections. In the hospital, patients will receive intravenous antibiotics and other supportive care. Hospitalization may also be necessary for patients who are unable to take oral medications or who have other medical conditions that complicate their treatment.
Treatment for diabetes infection is an important part of managing diabetes. By following their doctor’s orders and taking their medications as prescribed, people with diabetes can improve their chances of a full recovery.
Prevention
Preventing diabetes infection is essential for people with diabetes to maintain their health and well-being. This section explores the connection between prevention and diabetes infection, highlighting key aspects that contribute to effective prevention strategies.
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control: High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making people with diabetes more susceptible to infections. Keeping blood sugar levels under control through medication, diet, and exercise is crucial for preventing diabetes infection.
- Taking antibiotics as prescribed: Antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections. People with diabetes should take antibiotics exactly as prescribed by their doctor to ensure the infection is fully treated and to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
- Practicing good hygiene: Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, keeping wounds clean, and maintaining a clean environment, help prevent the spread of bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
These preventive measures are interconnected and work together to reduce the risk of diabetes infection. By following these recommendations, people with diabetes can take an active role in safeguarding their health and preventing the onset of infections.
Diabetes Infection FAQs
Diabetes infection is a serious complication that can lead to hospitalization and even death. Here are some frequently asked questions and answers about diabetes infection:
Question 1: What causes diabetes infection?
Answer: Diabetes infection can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. People with diabetes are more likely to develop infections because their immune system is weakened and their circulation is poor.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of diabetes infection?
Answer: Symptoms of diabetes infection can vary depending on the type of infection, but may include fever, chills, pain, swelling, and redness.
Question 3: How is diabetes infection treated?
Answer: Treatment for diabetes infection typically involves antibiotics or other medications, and may also require hospitalization.
Question 4: How can I prevent diabetes infection?
Answer: Preventing diabetes infection is important for people with diabetes. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, taking antibiotics as prescribed, and practicing good hygiene.
Question 5: What are the risk factors for diabetes infection?
Answer: People with diabetes are more likely to develop infections because their immune system is weakened and their circulation is poor.
Question 6: What are the types of diabetes infection?
Answer: The most common type of diabetes infection is a skin infection, but other types include pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis.
Summary: Diabetes infection is a serious complication that can be prevented and treated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of diabetes infection, people with diabetes can take steps to protect their health.
Next: Learn more about diabetes management
Tips for Preventing and Managing Diabetes Infection
Diabetes infection is a serious complication that can lead to hospitalization and even death. By following these tips, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of infection and improve their overall health.
Tip 1: Keep blood sugar levels under control. High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making people with diabetes more susceptible to infections. Keeping blood sugar levels under control through medication, diet, and exercise is crucial for preventing diabetes infection.
Tip 2: Take antibiotics as prescribed. Antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections. People with diabetes should take antibiotics exactly as prescribed by their doctor to ensure the infection is fully treated and to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
Tip 3: Practice good hygiene. Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, keeping wounds clean, and maintaining a clean environment, help prevent the spread of bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
Tip 4: Get vaccinated. Vaccinations can protect people with diabetes from certain types of infections, such as pneumonia and influenza. People with diabetes should talk to their doctor about which vaccinations are recommended for them.
Tip 5: Manage other health conditions. People with diabetes who have other health conditions, such as heart disease or kidney disease, are at an increased risk for infection. Managing these other health conditions can help to reduce the risk of infection.
Summary: By following these tips, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of infection and improve their overall health.
Next: Learn more about diabetes management
Diabetes Infection
Diabetes infection is a serious complication that can lead to hospitalization and even death. In this article, we have explored the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of diabetes infection. We have also provided tips for people with diabetes to reduce their risk of infection and improve their overall health.
Diabetes infection is a preventable and treatable complication. By following the tips in this article, people with diabetes can take steps to protect their health and prevent the onset of infection. If you have diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor about your risk of infection and how to prevent it.
Youtube Video: