Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
DKA is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment. If left untreated, DKA can lead to coma or death. DKA guidelines provide healthcare professionals with instructions on how to diagnose, treat, and prevent DKA. These guidelines are based on the latest scientific evidence and are updated regularly to ensure that patients receive the best possible care.
DKA guidelines are essential for the management of diabetes. They help healthcare professionals to provide timely and effective treatment, which can prevent serious complications. DKA guidelines also help to educate patients about DKA and its prevention.
diabetic ketoacidosis guidelines
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) guidelines are essential for the management of diabetes. They provide healthcare professionals with instructions on how to diagnose, treat, and prevent DKA. These guidelines are based on the latest scientific evidence and are updated regularly to ensure that patients receive the best possible care.
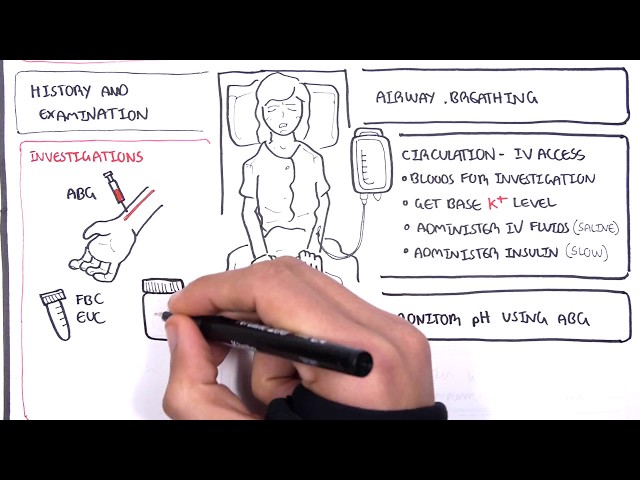
- Diagnosis: DKA guidelines provide criteria for diagnosing DKA, including blood glucose levels, ketone levels, and pH levels.
- Treatment: DKA guidelines recommend treatment with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. The goal of treatment is to correct the underlying metabolic abnormalities and prevent complications.
- Prevention: DKA guidelines recommend measures to prevent DKA, such as good blood glucose control, regular exercise, and a healthy diet.
- Education: DKA guidelines emphasize the importance of patient education about DKA and its prevention.
- Monitoring: DKA guidelines recommend regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and ketone levels to prevent DKA.
- Follow-up: DKA guidelines recommend follow-up care to ensure that patients are recovering well and to prevent future episodes of DKA.
These six key aspects of DKA guidelines are essential for the management of diabetes. By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can provide timely and effective treatment for DKA, prevent serious complications, and educate patients about DKA and its prevention.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing DKA is crucial for prompt and effective treatment. DKA guidelines provide clear criteria for diagnosing DKA, ensuring that healthcare professionals can accurately identify and manage this serious condition.
- Blood glucose levels: DKA guidelines specify the blood glucose levels that indicate DKA. High blood glucose levels are a hallmark of DKA, and they must be corrected to treat the condition.
- Ketone levels: DKA guidelines also provide criteria for ketone levels. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In DKA, the body produces high levels of ketones, which can lead to metabolic acidosis.
- pH levels: DKA guidelines include criteria for pH levels. pH levels measure the acidity or alkalinity of the blood. In DKA, the blood becomes acidic, and the pH level drops. Correcting the pH level is essential for treating DKA.
These diagnostic criteria are essential for the management of DKA. By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose DKA and provide timely and effective treatment.
Treatment
Treatment is a crucial component of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) guidelines. DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
DKA guidelines recommend treatment with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes to correct the underlying metabolic abnormalities and prevent complications. Fluids are given to replace the fluids that are lost through urination and dehydration. Insulin is given to lower blood glucose levels. Electrolytes are given to correct electrolyte imbalances.
The goal of treatment is to correct the underlying metabolic abnormalities and prevent complications. Treatment should be started as soon as possible to prevent serious complications, such as coma or death.
DKA guidelines are essential for the management of DKA. They provide healthcare professionals with instructions on how to diagnose, treat, and prevent DKA. By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can provide timely and effective treatment for DKA and prevent serious complications.
Prevention
Prevention is a crucial aspect of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) guidelines. DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Good blood glucose control: DKA guidelines emphasize the importance of good blood glucose control to prevent DKA. High blood glucose levels can lead to the production of ketones, so it is important to keep blood glucose levels within a healthy range.
- Regular exercise: Regular exercise can help to prevent DKA by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood glucose levels. Exercise also helps to burn fat, which can reduce the risk of producing ketones.
- Healthy diet: A healthy diet can help to prevent DKA by providing the body with the nutrients it needs to function properly. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
By following these preventive measures, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing DKA. DKA guidelines are essential for the management of diabetes. They provide healthcare professionals with instructions on how to diagnose, treat, and prevent DKA. By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can help people with diabetes to live healthy and fulfilling lives.
Education
Patient education is a crucial component of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) guidelines. DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
DKA guidelines emphasize the importance of patient education about DKA and its prevention because patients who are well-informed about DKA are more likely to be able to recognize the symptoms of DKA and take steps to prevent it. For example, patients who know that high blood glucose levels can lead to DKA are more likely to monitor their blood glucose levels regularly and take steps to keep their blood glucose levels within a healthy range.
In addition, patients who are well-informed about DKA are more likely to be able to recognize the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention promptly. This can help to prevent serious complications, such as coma or death.
DKA guidelines recommend that healthcare professionals provide patients with education about DKA, including the following information:
- What is DKA
- What are the symptoms of DKA
- How to prevent DKA
- What to do if you think you have DKA
Patient education is an essential component of DKA guidelines. By providing patients with information about DKA, healthcare professionals can help patients to prevent DKA and to recognize and seek treatment for DKA promptly.
Monitoring
Monitoring blood glucose levels and ketone levels is a crucial component of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) guidelines. DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels: DKA guidelines recommend regular monitoring of blood glucose levels to prevent DKA. High blood glucose levels can lead to the production of ketones. By monitoring blood glucose levels regularly, people with diabetes can identify and address high blood glucose levels before they lead to DKA.
- Regular monitoring of ketone levels: DKA guidelines also recommend regular monitoring of ketone levels to prevent DKA. Ketone levels can rise quickly in people with diabetes, so it is important to monitor ketone levels regularly to identify and address high ketone levels before they lead to DKA.
By following these monitoring recommendations, people with diabetes can help to prevent DKA. DKA guidelines are essential for the management of diabetes. They provide healthcare professionals with instructions on how to diagnose, treat, and prevent DKA. By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can help people with diabetes to live healthy and fulfilling lives.
Follow-up
Follow-up care is an essential component of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) guidelines. DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
Follow-up care after an episode of DKA is important to ensure that the patient is recovering well and to prevent future episodes of DKA. Follow-up care may include:
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and ketone levels
- Education about DKA, including how to prevent and recognize the symptoms of DKA
- Referral to a diabetes care and education specialist
- Medical nutrition therapy
- Exercise counseling
By following these recommendations, patients can help to prevent future episodes of DKA and live healthy and fulfilling lives.
FAQs on Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Guidelines
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that requires prompt medical attention. DKA guidelines provide healthcare professionals with instructions on how to diagnose, treat, and prevent DKA. These guidelines are based on the latest scientific evidence and are updated regularly to ensure that patients receive the best possible care.
Question 1: What are the symptoms of DKA?
DKA can cause a range of symptoms, including: high blood glucose levels, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, dehydration, confusion, and loss of consciousness. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Question 2: How is DKA treated?
Treatment for DKA typically involves fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Fluids are given to replace the fluids that are lost through urination and dehydration. Insulin is given to lower blood glucose levels. Electrolytes are given to correct electrolyte imbalances.
Question 3: Can DKA be prevented?
Yes, DKA can be prevented by following these steps: controlling blood glucose levels, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medications as prescribed by your doctor.
Question 4: What are the long-term risks of DKA?
DKA can lead to serious long-term complications, such as kidney damage, blindness, and heart disease. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions to prevent DKA and its complications.
Question 5: How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels?
The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on your individual needs and your doctor’s recommendations. Generally, people with diabetes should check their blood glucose levels several times a day.
Question 6: What should I do if I think I have DKA?
If you think you may have DKA, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. DKA is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and treated. By following your doctor’s instructions, you can help to reduce your risk of DKA and live a healthy life with diabetes.
Transition to the next article section:
[Insert link or text to the next section of the article]
Tips to Prevent and Manage Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be prevented and managed by following these tips:
Tip 1: Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly.
Regular blood glucose monitoring helps you to identify and address high blood glucose levels before they lead to DKA. Aim to check your blood glucose levels several times a day, or as directed by your doctor.
Tip 2: Follow a healthy diet.
Eating a healthy diet helps to control blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of DKA. Choose foods that are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Tip 3: Get regular exercise.
Regular exercise helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Tip 4: Take your medications as prescribed.
Taking your diabetes medications as prescribed helps to control blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of DKA. Do not skip or stop taking your medications without talking to your doctor.
Tip 5: Recognize the symptoms of DKA.
Early recognition of DKA symptoms is crucial. If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek medical attention immediately: high blood glucose levels, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, dehydration, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Tip 6: Follow your doctor’s instructions.
Your doctor is the best source of information about DKA prevention and management. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and ask questions if you have any concerns.
Tip 7: Carry a medical ID.
In case of an emergency, a medical ID can alert healthcare professionals that you have diabetes and are at risk for DKA. Wear a medical ID bracelet or necklace, or carry a medical ID card in your wallet.
Tip 8: Educate yourself about DKA.
The more you know about DKA, the better you can prevent and manage it. Talk to your doctor, read books and articles, and attend diabetes education classes to learn more about DKA.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By following these tips, you can help to prevent and manage DKA and live a healthy life with diabetes.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
[Insert link or text to the conclusion of the article]
Conclusion
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) guidelines are essential for the management of diabetes. They provide healthcare professionals with instructions on how to diagnose, treat, and prevent DKA. These guidelines are based on the latest scientific evidence and are updated regularly to ensure that patients receive the best possible care.
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be prevented and treated. By following DKA guidelines, healthcare professionals can help people with diabetes to live healthy and fulfilling lives. Patients and caregivers should work closely with their healthcare team to understand and follow DKA guidelines to prevent and manage this serious condition.
Youtube Video: