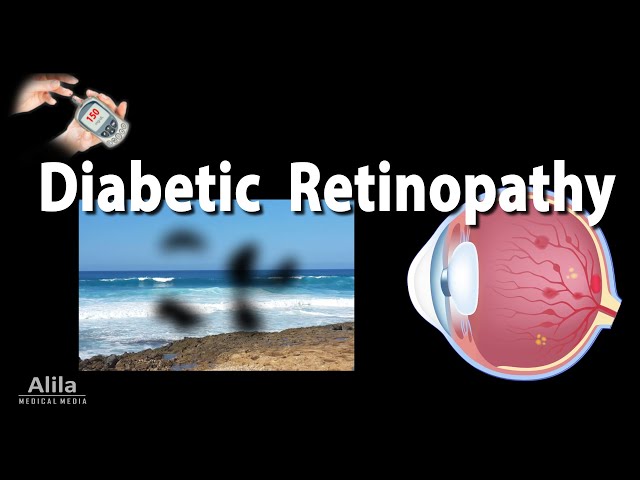
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. It is a complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness in people with the condition. Diabetic retinopathy can cause a range of symptoms, including blurred vision, floaters, and dark spots in the vision. In severe cases, it can lead to blindness.
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina. This damage can occur over time as a result of high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can cause the blood vessels to become narrow and blocked, which can lead to a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the retina. This can damage the retina and lead to the development of diabetic retinopathy.
There are a number of risk factors for diabetic retinopathy, including:
- Having diabetes for a long time
- Having high blood sugar levels
- Having high blood pressure
- Being overweight or obese
- Having high cholesterol
- Being a smoker
Diabetic retinopathy can be diagnosed with a comprehensive eye exam, which includes dilating the pupils and examining the retina. Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the severity of the condition. Treatment options may include:
- Laser therapy
- Anti-VEGF injections
- Surgery
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious condition that can lead to blindness. However, early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss. If you have diabetes, it is important to have regular eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy.
diabetic retinopothy
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness in people with the condition.
- Symptoms: Blurred vision, floaters, dark spots
- Causes: High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels in the retina
- Risk factors: Diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking
- Diagnosis: Comprehensive eye exam with dilated pupils
- Treatment: Laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, surgery
- Prevention: Control blood sugar levels, regular eye exams
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious condition, but it can be prevented and treated. If you have diabetes, it is important to have regular eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss.
Symptoms
Blurred vision, floaters, and dark spots are all common symptoms of diabetic retinopathy. These symptoms occur when the blood vessels in the retina are damaged, which can lead to a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the retina. This damage can cause the retina to swell and leak fluid, which can lead to blurred vision. Floaters are small, dark spots that appear in the field of vision. They are caused by clumps of blood or other debris in the vitreous, the gel-like substance that fills the eye. Dark spots are areas of the retina that have been damaged and are no longer able to function properly.
- Blurred vision is a common symptom of diabetic retinopathy. It can be caused by swelling of the retina, which can occur when the blood vessels in the retina are damaged. Blurred vision can also be caused by bleeding in the vitreous, the gel-like substance that fills the eye.
- Floaters are small, dark spots that appear in the field of vision. They are caused by clumps of blood or other debris in the vitreous. Floaters are a common symptom of diabetic retinopathy, but they can also be caused by other conditions, such as aging or eye inflammation.
- Dark spots are areas of the retina that have been damaged and are no longer able to function properly. Dark spots can be caused by bleeding in the retina, or by the formation of scar tissue. Dark spots are a serious symptom of diabetic retinopathy, and they can lead to vision loss.
If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor right away. Early diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy can help to prevent vision loss.
Causes
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This damage can occur over time as a result of high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can cause the blood vessels to become narrow and blocked, which can lead to a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the retina. This can damage the retina and lead to the development of diabetic retinopathy.
- Hyperglycemia: When blood sugar levels are too high, it can damage the blood vessels in the retina. This damage can lead to the development of diabetic retinopathy.
- Oxidative stress: High blood sugar levels can also lead to oxidative stress, which is a process that can damage cells and tissues. Oxidative stress can contribute to the development of diabetic retinopathy.
- Inflammation: High blood sugar levels can also lead to inflammation, which is a process that can damage blood vessels. Inflammation can contribute to the development of diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious condition that can lead to blindness. However, early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss. If you have diabetes, it is important to have regular eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy.
Risk factors
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness in people with the condition.
There are a number of risk factors for diabetic retinopathy, including:
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. The longer a person has diabetes, the greater their risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the retina, making them more likely to develop diabetic retinopathy.
- High cholesterol: High cholesterol can also damage the blood vessels in the retina, making them more likely to develop diabetic retinopathy.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels throughout the body, including the blood vessels in the retina. This can increase the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
It is important to control these risk factors to reduce the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. People with diabetes should have their blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels checked regularly. They should also quit smoking.
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious condition, but it can be prevented and treated. If you have diabetes, it is important to have regular eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss.
Diagnosis
A comprehensive eye exam with dilated pupils is the gold standard for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy. It is a painless procedure that takes about 30 minutes. During the exam, the doctor will use a special instrument to widen (dilate) the pupils. This allows the doctor to see the back of the eye, including the retina, more clearly.
-
The doctor will look for signs of diabetic retinopathy, such as:
– Swelling of the retina – Bleeding in the retina – Formation of new blood vessels – Damage to the blood vessels in the retina
-
The doctor may also take photographs of the back of the eye to track the progression of diabetic retinopathy over time.
Regular eye exams are important for people with diabetes, even if they do not have any symptoms of diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy can help to prevent vision loss.
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness. However, early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss. If you have diabetes, it is important to have regular eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy.
Treatment
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness in people with the condition.
There are a number of treatments for diabetic retinopathy, including:
- Laser therapy is a procedure in which a laser is used to seal leaking blood vessels in the retina.
- Anti-VEGF injections are injections that are used to block the growth of new blood vessels in the retina.
- Surgery is sometimes necessary to remove scar tissue or other blockages from the retina.
The goal of treatment for diabetic retinopathy is to prevent vision loss. Treatment can be effective in slowing or stopping the progression of the condition, but it cannot reverse damage that has already occurred.
It is important for people with diabetes to have regular eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss.
Prevention
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness in people with the condition.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent or slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy, including:
- Control blood sugar levels: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, so it is important for people with diabetes to keep their blood sugar levels under control.
- Have regular eye exams: Regular eye exams can help to detect diabetic retinopathy early, when it is easier to treat. People with diabetes should have an eye exam at least once a year.
Controlling blood sugar levels and having regular eye exams are two of the most important things that people with diabetes can do to prevent or slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy. By following these recommendations, people with diabetes can help to protect their vision and reduce their risk of blindness.
Diabetic Retinopathy FAQs
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness in people with the condition.
Here are some frequently asked questions about diabetic retinopathy:
Question 1: What are the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
The early stages of diabetic retinopathy often have no symptoms. As the condition progresses, symptoms may include blurred vision, floaters, dark spots, and vision loss.
Question 2: What are the risk factors for diabetic retinopathy?
The risk factors for diabetic retinopathy include having diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and being overweight or obese.
Question 3: How is diabetic retinopathy diagnosed?
Diabetic retinopathy is diagnosed with a comprehensive eye exam, which includes dilating the pupils and examining the retina.
Question 4: How is diabetic retinopathy treated?
The treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the severity of the condition. Treatment options may include laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, and surgery.
Question 5: Can diabetic retinopathy be prevented?
Diabetic retinopathy can be prevented by controlling blood sugar levels and having regular eye exams.
Question 6: What is the prognosis for diabetic retinopathy?
The prognosis for diabetic retinopathy depends on the severity of the condition and how early it is diagnosed and treated. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss.
If you have diabetes, it is important to have regular eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss.
To learn more about diabetic retinopathy, please visit the following resources:
- National Eye Institute
- American Diabetes Association
- Mayo Clinic
Tips for Preventing and Managing Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness in people with the condition.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent or slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy, including:
Tip 1: Control blood sugar levels
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, so it is important for people with diabetes to keep their blood sugar levels under control. This can be done by taking medication as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Tip 2: Have regular eye exams
Regular eye exams can help to detect diabetic retinopathy early, when it is easier to treat. People with diabetes should have an eye exam at least once a year.
Tip 3: Quit smoking
Smoking damages the blood vessels throughout the body, including the blood vessels in the retina. Quitting smoking can help to reduce the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
Tip 4: Maintain a healthy weight
Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. Maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk of developing the condition.
Tip 5: Control blood pressure
High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the retina, so it is important for people with diabetes to control their blood pressure. This can be done by taking medication as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Tip 6: Control cholesterol levels
High cholesterol can damage the blood vessels in the retina, so it is important for people with diabetes to control their cholesterol levels. This can be done by taking medication as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Tip 7: Eat a healthy diet
Eating a healthy diet can help to control blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. A healthy diet for people with diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Tip 8: Get regular exercise
Getting regular exercise can help to control blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Exercise can also help to maintain a healthy weight.
By following these tips, people with diabetes can help to prevent or slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss.
If you have diabetes, it is important to have regular eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to protect your vision and reduce your risk of blindness.
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness in people with the condition.
There are a number of risk factors for diabetic retinopathy, including having diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and being overweight or obese. Diabetic retinopathy can be prevented by controlling blood sugar levels, having regular eye exams, and quitting smoking. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent vision loss.
If you have diabetes, it is important to have regular eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to protect your vision and reduce your risk of blindness.
Youtube Video: