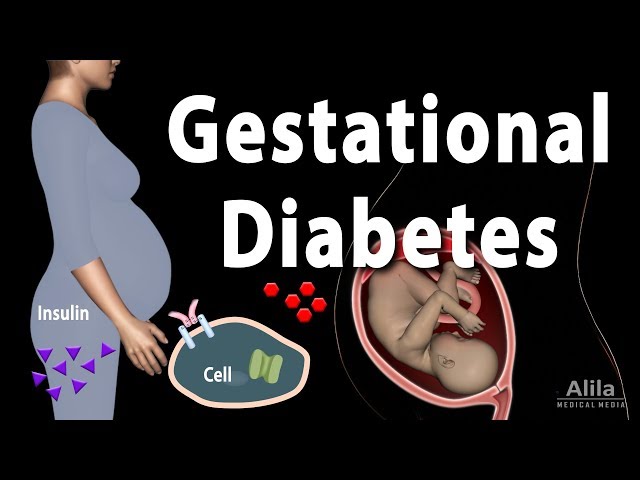
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually develops in the second or third trimester and goes away after the baby is born. Gestational diabetes causes high blood sugar levels that can harm both the mother and the baby if not managed properly.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. By following their doctor’s recommendations, women with gestational diabetes can have a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
If you are pregnant, it is important to get regular prenatal care so that your doctor can check for gestational diabetes. If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, your doctor will work with you to develop a management plan that is right for you.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a serious but manageable condition that can occur during pregnancy. It is important to understand the key aspects of gestational diabetes in order to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
- Definition: Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy.
- Causes: Gestational diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin during pregnancy.
- Symptoms: Gestational diabetes often has no symptoms, but some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
- Diagnosis: Gestational diabetes is diagnosed with a glucose tolerance test.
- Treatment: Gestational diabetes is treated with diet, exercise, and medication.
- Risks: Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of pregnancy complications, such as pre-eclampsia and premature birth.
- Prevention: There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, but eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk.
- Management: Women with gestational diabetes can manage their condition by following their doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and medication.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By understanding the key aspects of gestational diabetes, women can take steps to reduce their risk, ensure a healthy pregnancy, and deliver a healthy baby.
Definition
Gestational diabetes is a serious but common condition that affects pregnant women. It is important to understand the definition of gestational diabetes and its connection to diabetes in order to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
- Gestational diabetes is a temporary condition. Unlike other types of diabetes, gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Gestational diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy. During pregnancy, the body produces more glucose, which can lead to high blood sugar levels if the body cannot produce enough insulin.
- Gestational diabetes can have serious consequences for both the mother and the baby. High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of pregnancy complications, such as pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and macrosomia (a large baby). Gestational diabetes can also increase the risk of birth defects and other health problems for the baby.
- Gestational diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. By following their doctor’s recommendations, women with gestational diabetes can control their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By understanding the definition of gestational diabetes and its connection to diabetes, women can take steps to reduce their risk, ensure a healthy pregnancy, and deliver a healthy baby.
Causes
Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy. During pregnancy, the body produces more glucose, which can lead to high blood sugar levels if the body cannot produce enough insulin. This can lead to gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to the development of gestational diabetes, including:
- Obesity
- Age (over 25)
- Family history of diabetes
- History of gestational diabetes
- Certain ethnicities (African American, Hispanic, Asian, Native American)
Gestational diabetes can have serious consequences for both the mother and the baby. High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of pregnancy complications, such as pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and macrosomia (a large baby). Gestational diabetes can also increase the risk of birth defects and other health problems for the baby.
Gestational diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. By following their doctor’s recommendations, women with gestational diabetes can control their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications.
Symptoms
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can cause a number of symptoms, including increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
These symptoms are often mild and may not be noticeable at first. However, if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor right away. Untreated gestational diabetes can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the baby.
In addition to the symptoms listed above, some women with gestational diabetes may also experience blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor right away.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. By following your doctor’s recommendations, you can control your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of complications.
Diagnosis
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can cause a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby.
The glucose tolerance test is a blood test that is used to diagnose gestational diabetes. The test is usually performed between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy. During the test, you will be asked to drink a sugary drink and then have your blood sugar levels checked at regular intervals.
If your blood sugar levels are too high, you will be diagnosed with gestational diabetes. Your doctor will then work with you to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
- The glucose tolerance test is a safe and effective way to diagnose gestational diabetes. The test is usually performed in a doctor’s office or clinic and takes about 2 hours to complete.
- The glucose tolerance test is not a fasting test. You will be asked to eat a normal meal before the test.
- The glucose tolerance test is not a test for type 1 or type 2 diabetes. These types of diabetes are not caused by pregnancy.
If you are pregnant, it is important to get regular prenatal care so that your doctor can check for gestational diabetes. If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Treatment
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can cause a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby.
Treatment for gestational diabetes focuses on controlling blood sugar levels. This can be done through diet, exercise, and medication.
- Diet: Eating a healthy diet is an important part of managing gestational diabetes. A healthy diet for gestational diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also includes lean protein and low-fat dairy products.
- Exercise: Exercise is another important part of managing gestational diabetes. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting an exercise program during pregnancy.
- Medication: Medication may be necessary to control blood sugar levels in some women with gestational diabetes. There are a number of different medications that can be used to treat gestational diabetes. Your doctor will work with you to choose the best medication for you.
Treatment for gestational diabetes is important for both the mother and the baby. By controlling blood sugar levels, treatment can help to reduce the risk of pregnancy complications, such as pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and macrosomia (a large baby). Treatment can also help to reduce the risk of birth defects and other health problems for the baby.
Risks
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of pregnancy complications, including pre-eclampsia and premature birth. Pre-eclampsia is a condition characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine, while premature birth is the birth of a baby before 37 weeks of gestation.
-
Pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication that can lead to seizures, stroke, and even death for both the mother and the baby. It is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Gestational diabetes increases the risk of pre-eclampsia by two to four times.
-
Premature birth
Premature birth is the birth of a baby before 37 weeks of gestation. Babies born prematurely are at an increased risk of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays. Gestational diabetes increases the risk of premature birth by two to three times.
-
Other pregnancy complications
Gestational diabetes can also increase the risk of other pregnancy complications, such as macrosomia (a large baby), polyhydramnios (too much amniotic fluid), and placental abruption (the placenta separates from the uterus before the baby is born). These complications can all lead to serious health problems for both the mother and the baby.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By following their doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and medication, women with gestational diabetes can reduce their risk of pregnancy complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Prevention
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of pregnancy complications, including pre-eclampsia and premature birth. However, there is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes. Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk, but these measures are not guaranteed to prevent the condition.
The best way to reduce your risk of gestational diabetes is to make healthy lifestyle choices before you become pregnant. This includes eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight. If you are overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can help to reduce your risk of gestational diabetes.
It is also important to control your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes or are at risk for diabetes. This can be done by taking medication, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, talk to your doctor about your risk of gestational diabetes. Your doctor can recommend ways to reduce your risk and monitor your blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
Management
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of pregnancy complications, including pre-eclampsia and premature birth. However, gestational diabetes can be managed with proper care. By following their doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and medication, women with gestational diabetes can control their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of pregnancy complications.
-
Diet
Eating a healthy diet is an important part of managing gestational diabetes. A healthy diet for gestational diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also includes lean protein and low-fat dairy products. Eating a healthy diet can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
-
Exercise
Exercise is another important part of managing gestational diabetes. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting an exercise program during pregnancy. Exercise can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
-
Medication
Medication may be necessary to control blood sugar levels in some women with gestational diabetes. There are a number of different medications that can be used to treat gestational diabetes. Your doctor will work with you to choose the best medication for you. Medication can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
Managing gestational diabetes is important for both the mother and the baby. By following their doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and medication, women with gestational diabetes can reduce their risk of pregnancy complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Gestational Diabetes FAQs
Gestational diabetes is a serious but manageable condition that can occur during pregnancy. It is important to understand the key aspects of gestational diabetes in order to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery. The following are some frequently asked questions about gestational diabetes:
Question 1: What is gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes often has no symptoms, but some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
Question 3: How is gestational diabetes diagnosed?
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed with a glucose tolerance test. The test is usually performed between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy.
Question 4: How is gestational diabetes treated?
Gestational diabetes is treated with diet, exercise, and medication. By following their doctor’s recommendations, women with gestational diabetes can control their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications.
Question 5: What are the risks of gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of pregnancy complications, such as pre-eclampsia and premature birth.
Question 6: Can gestational diabetes be prevented?
There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, but eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By understanding the key aspects of gestational diabetes, women can take steps to reduce their risk and ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Transition to the next article section:
For more information on gestational diabetes, please visit the following resources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
Gestational Diabetes Management Tips
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can occur during pregnancy. By following these tips, women with gestational diabetes can manage their condition and reduce their risk of complications.
Tip 1: Follow a healthy diet.
Eating a healthy diet is an important part of managing gestational diabetes. A healthy diet for gestational diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also includes lean protein and low-fat dairy products. Eating a healthy diet can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
Tip 2: Exercise regularly.
Exercise is another important part of managing gestational diabetes. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting an exercise program during pregnancy. Exercise can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
Tip 3: Monitor your blood sugar levels.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is important for managing gestational diabetes. Your doctor will recommend how often you should check your blood sugar levels. Monitoring your blood sugar levels can help you to make sure that your blood sugar levels are under control.
Tip 4: Take medication as prescribed.
Medication may be necessary to control blood sugar levels in some women with gestational diabetes. Your doctor will work with you to choose the best medication for you. Taking medication as prescribed can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
Tip 5: Get regular prenatal care.
Getting regular prenatal care is important for all pregnant women, including women with gestational diabetes. Prenatal care can help to monitor your health and your baby’s health. Your doctor will also be able to provide you with support and guidance on managing your gestational diabetes.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By following these tips, women with gestational diabetes can manage their condition and reduce their risk of pregnancy complications. Managing gestational diabetes is important for both the mother and the baby. By following their doctor’s recommendations, women with gestational diabetes can ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
For more information on gestational diabetes, please visit the following resources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
Conclusion
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can occur during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can cause a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby.
Gestational diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. By following their doctor’s recommendations, women with gestational diabetes can control their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of pregnancy complications. It is important for women with gestational diabetes to get regular prenatal care so that their doctor can monitor their health and the health of their baby.
Youtube Video: