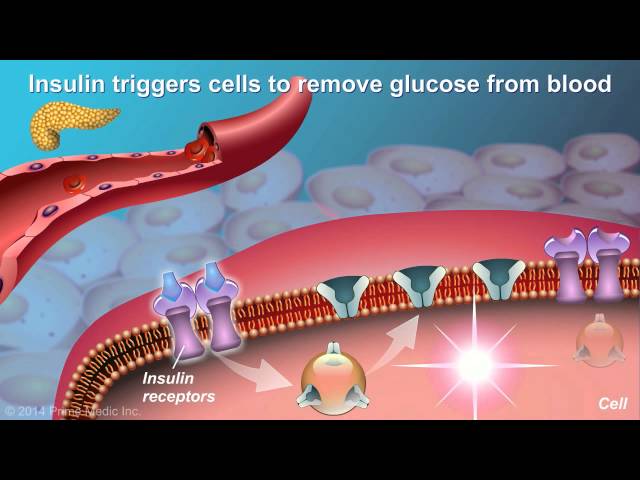
Diabetes 2, also known as type 2 diabetes, is a chronic condition that affects the way the body uses sugar (glucose). Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells for energy. With type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t make enough insulin or doesn’t use insulin well. This can lead to high blood sugar levels.
There are many risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes, including:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of diabetes
- Age (over 45)
- Race/ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are at increased risk)
- Certain medical conditions, such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or Gestational Diabetes
There is no cure for type 2 diabetes, but it can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. Treatment aims to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range. This can help prevent or delay complications of diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
If you have any of the risk factors for type 2 diabetes, talk to your doctor about ways to prevent or delay the onset of the disease.
How Do You Get Diabetes 2?
Diabetes 2, also known as type 2 diabetes, is a chronic condition that affects the way the body uses sugar (glucose). There are many risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes, but the exact cause is unknown. Some of the key aspects that may contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes include:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of diabetes
- Age (over 45)
- Race/ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are at increased risk)
- Certain medical conditions, such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or Gestational Diabetes
- Unhealthy diet
- Smoking
These are just some of the key aspects that may contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. It is important to note that not everyone who has these risk factors will develop type 2 diabetes. However, people who have multiple risk factors are more likely to develop the disease.
If you are concerned about your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, talk to your doctor. They can help you assess your risk and develop a plan to reduce your risk of developing the disease.
Obesity
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. In fact, people who are obese are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people who are not obese. There are several reasons for this.
First, obesity can lead to insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells for energy. When a person is obese, the cells in the body become less responsive to insulin. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes.
Second, obesity can also lead to inflammation. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can damage the cells and tissues in the body, including the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This can also lead to high blood sugar levels and type 2 diabetes.
There are many things that people can do to reduce their risk of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes, including eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Losing even a small amount of weight can help to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. For example, a study published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine found that people who lost 5% of their body weight over a period of 6 months were 58% less likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people who did not lose weight.
If you are obese, talk to your doctor about ways to lose weight and reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Physical inactivity
Physical inactivity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. When a person is physically inactive, their muscles do not use glucose for energy as efficiently. This can lead to a build-up of glucose in the blood, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes.
-
Reduced insulin sensitivity
Physical inactivity can lead to reduced insulin sensitivity. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells for energy. When a person is physically inactive, the cells in the body become less responsive to insulin. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes.
-
Increased inflammation
Physical inactivity can also lead to increased inflammation. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can damage the cells and tissues in the body, including the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This can also lead to high blood sugar levels and type 2 diabetes.
-
Weight gain
Physical inactivity can also lead to weight gain. Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. In fact, people who are obese are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people who are not obese.
-
Other factors
In addition to the factors listed above, physical inactivity can also lead to other health problems that can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
There is strong evidence to support the link between physical inactivity and type 2 diabetes. For example, a study published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine found that people who were physically inactive were more than twice as likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people who were physically active.
If you are concerned about your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, talk to your doctor about ways to increase your physical activity level.
Family history of diabetes
Family history of diabetes is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. In fact, people who have a family history of diabetes are more likely to develop the disease than people who do not have a family history of diabetes.
-
Genetics
Diabetes is a complex disease that is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. If you have a family history of diabetes, you are more likely to inherit the genes that increase your risk of developing the disease.
-
Lifestyle
People who have a family history of diabetes are also more likely to share similar lifestyle factors that can increase the risk of developing the disease, such as obesity and physical inactivity.
-
Environment
People who have a family history of diabetes are also more likely to be exposed to environmental factors that can increase the risk of developing the disease, such as exposure to pollutants or certain chemicals.
-
Other factors
There are other factors that can also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, such as age, race/ethnicity, and certain medical conditions. However, family history of diabetes is one of the strongest risk factors for the disease.
If you have a family history of diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk of developing the disease. There are many things that you can do to reduce your risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Age (over 45)
Age is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases with age, and people over the age of 45 are at an increased risk of developing the disease. There are several reasons for this:
-
Decreased insulin sensitivity
As people age, their cells become less responsive to insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells for energy. When cells are less responsive to insulin, glucose can build up in the blood, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes. -
Reduced physical activity
As people age, they are often less physically active than they were when they were younger. Physical inactivity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. When people are physically inactive, their muscles do not use glucose for energy as efficiently. This can lead to a build-up of glucose in the blood, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes. -
Weight gain
As people age, they often gain weight. Weight gain is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Obesity can lead to insulin resistance, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes. -
Other factors
There are other factors that can also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, such as family history of diabetes, race/ethnicity, and certain medical conditions. However, age is one of the strongest risk factors for the disease.
It is important to be aware of the increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes as you age. There are many things that you can do to reduce your risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. If you are over the age of 45, talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Race/ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are at increased risk)
Race and ethnicity are important factors that can influence a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Research has shown that certain racial and ethnic groups are at an increased risk of developing the disease, including African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans.
-
Genetic factors
There is evidence to suggest that genetic factors may play a role in the increased risk of type 2 diabetes among certain racial and ethnic groups. For example, studies have shown that African Americans have a higher prevalence of certain genetic variants that are associated with an increased risk of developing the disease.
-
Social and environmental factors
In addition to genetic factors, social and environmental factors are also thought to contribute to the increased risk of type 2 diabetes among certain racial and ethnic groups. For example, African Americans and Hispanic Americans are more likely to live in poverty, which is a risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, these groups are more likely to have limited access to healthy food and safe places to exercise, which can also contribute to the increased risk of developing the disease.
-
Cultural factors
Cultural factors can also play a role in the increased risk of type 2 diabetes among certain racial and ethnic groups. For example, some cultures may have traditional diets that are high in unhealthy fats and processed foods, which can contribute to weight gain and obesity, which are both risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes.
-
Other factors
There are a number of other factors that may also contribute to the increased risk of type 2 diabetes among certain racial and ethnic groups, including lack of access to healthcare, discrimination, and stress.
Understanding the complex relationship between race/ethnicity and type 2 diabetes is important for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By addressing the social, environmental, and cultural factors that contribute to the increased risk of type 2 diabetes among certain racial and ethnic groups, we can help to reduce the burden of this disease.
Certain medical conditions, such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or Gestational Diabetes
Certain medical conditions, such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or Gestational Diabetes, can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. These conditions can affect the way the body uses insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and eventually type 2 diabetes.
-
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by irregular periods, high levels of androgens (male hormones), and the development of cysts on the ovaries. Women with PCOS are more likely to develop insulin resistance, which can lead to type 2 diabetes.
-
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the placenta producing hormones that can block the effects of insulin. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy, but women who have had gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
If you have PCOS or gestational diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. There are many things that you can do to reduce your risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Unhealthy diet
Unhealthy diet is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. Eating a diet high in saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol, and sodium can increase your risk of developing the disease. Additionally, eating a diet low in fiber can also increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
-
Saturated and trans fats
Saturated and trans fats are found in many processed foods, such as fried foods, fatty meats, and processed snacks. These fats can raise your cholesterol levels, which can increase your risk of developing heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
-
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a type of fat that is found in animal products, such as meat, eggs, and dairy products. Eating a diet high in cholesterol can increase your cholesterol levels, which can increase your risk of developing heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
-
Sodium
Sodium is a type of mineral that is found in many processed foods, such as canned soups, processed meats, and salty snacks. Eating a diet high in sodium can increase your blood pressure, which can increase your risk of developing heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
-
Fiber
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Eating a diet high in fiber can help to lower your cholesterol levels and improve your blood sugar control, which can reduce your risk of developing heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Eating a healthy diet is an important part of reducing your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By eating a diet low in saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol, and sodium, and high in fiber, you can help to improve your overall health and reduce your risk of developing the disease.
Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. In fact, people who smoke are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people who do not smoke. There are several reasons for this.
First, smoking can damage the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells for energy. When the pancreas is damaged, it cannot produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and eventually type 2 diabetes.
Second, smoking can also lead to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a condition in which the cells in the body do not respond to insulin as well as they should. This can also lead to high blood sugar levels and eventually type 2 diabetes.
Third, smoking can also increase inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can damage the cells and tissues in the body, including the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This can also lead to high blood sugar levels and eventually type 2 diabetes.
There is strong evidence to support the link between smoking and type 2 diabetes. For example, a study published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine found that people who smoked were more than twice as likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people who did not smoke.
If you are concerned about your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, quitting smoking is one of the most important things you can do to reduce your risk.
FAQs on Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to use sugar (glucose) for energy. It is a major public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide.
Question 1: What are the main risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes?
Answer: There are several risk factors for type 2 diabetes, including obesity, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, age (over 45), race/ethnicity, and certain medical conditions such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or Gestational Diabetes.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Type 2 diabetes often develops gradually, and many people do not experience any symptoms in the early stages. However, as blood sugar levels rise, symptoms may develop, including frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores.
Question 3: How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
Answer: Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed through a blood test that measures blood sugar levels. A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes.
Question 4: How is type 2 diabetes treated?
Answer: Treatment for type 2 diabetes typically includes lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. Medications may also be prescribed to lower blood sugar levels.
Question 5: What are the complications of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes can lead to several complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and amputation.
Question 6: Can type 2 diabetes be prevented?
Answer: While there is no guaranteed way to prevent type 2 diabetes, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing the condition. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding tobacco use.
Summary: Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition that requires proper management to prevent complications. Early diagnosis and lifestyle modifications are crucial for effective diabetes management. If you have any concerns about your risk of developing type 2 diabetes or are experiencing any symptoms, do not hesitate to consult your healthcare provider.
Transition to the next article section: For more information on the causes and risk factors of type 2 diabetes, please refer to the next section.
Tips to Reduce Your Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a serious chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there is no cure for type 2 diabetes, there are many things you can do to reduce your risk of developing the disease. Here are five tips to help you get started:
Tip 1: Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Losing even a small amount of weight can help to reduce your risk. Aim to reach and maintain a healthy weight for your height and age.
Tip 2: Eat a Healthy Diet
Eating a healthy diet is essential for managing your weight and reducing your risk of type 2 diabetes. Focus on eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated and unhealthy fats.
Tip 3: Get Regular Exercise
Regular exercise helps to improve your insulin sensitivity and lower your blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Tip 4: Quit Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Quitting smoking can help to improve your overall health and reduce your risk of developing the disease.
Tip 5: Manage Your Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are both risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Talk to your doctor about ways to manage your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Summary: Reducing your risk of developing type 2 diabetes requires adopting a healthy lifestyle. By following these tips, you can improve your overall health and well-being and lower your risk of developing this serious chronic condition.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: For more information on type 2 diabetes, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, please refer to the rest of the article.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a complex disease with multiple contributing factors. This article has explored the various aspects that can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes, including obesity, physical inactivity, family history, age, race/ethnicity, certain medical conditions, unhealthy diet, and smoking.
Understanding the causes of type 2 diabetes is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing underlying health conditions, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing this serious chronic disease. Early diagnosis, proper management, and ongoing support are essential for individuals living with type 2 diabetes to achieve optimal health outcomes and prevent complications.
Youtube Video: