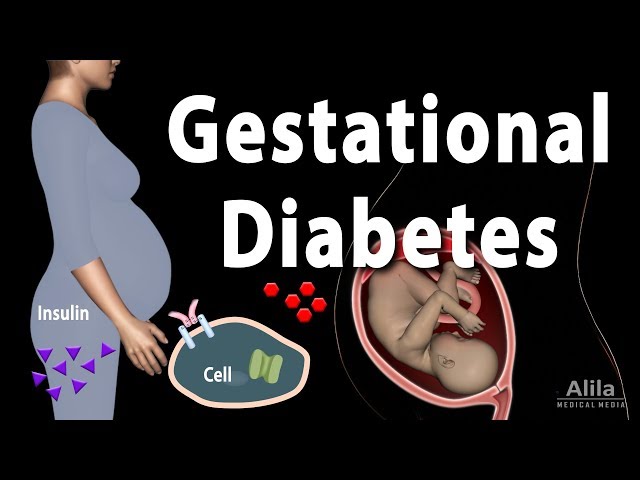
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, however without proper management it can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. Some of these complications can potentially impact the health of both the mother and the baby.
Gestational diabetes is caused by the placenta, which produces hormones that can make it difficult for the body to use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells. When the body can’t use insulin properly, blood sugar levels can get too high.
If you have gestational diabetes, you will need to monitor your blood sugar levels and eat a healthy diet. You may also need to take insulin to help control your blood sugar levels. By following your doctor’s instructions, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and reduce your risk of complications.
What Happens If You Get Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. Some of these complications can potentially impact the health of both the mother and the baby.
- High blood sugar levels – This can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby, including pre-eclampsia, macrosomia, and premature birth.
- Pre-eclampsia – This is a condition that can develop during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. It can lead to serious health problems for both the mother and the baby.
- Macrosomia – This is a condition in which the baby is born with a high birth weight. Macrosomia can increase the risk of complications during delivery, such as shoulder dystocia and birth injuries.
- Premature birth – This is when the baby is born before 37 weeks of gestation. Premature babies are at risk for a number of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays.
- Cesarean delivery – This is a surgical procedure to deliver the baby. Cesarean delivery may be necessary if the mother has gestational diabetes and is at risk for complications during delivery.
- Insulin therapy – This is a treatment for gestational diabetes that involves taking insulin to help control blood sugar levels.
- Diet and exercise – These are important parts of managing gestational diabetes. Eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise can help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels – This is important for managing gestational diabetes. Blood sugar levels should be checked regularly to make sure they are within a healthy range.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on the health of both the mother and the baby. However, by following your doctor’s instructions, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and reduce your risk of complications.
High blood sugar levels – This can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby, including pre-eclampsia, macrosomia, and premature birth.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the placenta producing hormones that can make it difficult for the body to use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells.
When the body can’t use insulin properly, blood sugar levels can get too high. This is known as hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia can lead to a number of complications during pregnancy, including pre-eclampsia, macrosomia, and premature birth.
- Pre-eclampsia is a condition that can develop during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. It can lead to serious health problems for both the mother and the baby.
- Macrosomia is a condition in which the baby is born with a high birth weight. Macrosomia can increase the risk of complications during delivery, such as shoulder dystocia and birth injuries.
- Premature birth is when the baby is born before 37 weeks of gestation. Premature babies are at risk for a number of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays.
It is important to manage blood sugar levels during pregnancy to reduce the risk of these complications. This can be done by eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking insulin if necessary.
Pre-eclampsia – This is a condition that can develop during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. It can lead to serious health problems for both the mother and the baby.
Pre-eclampsia is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Pre-eclampsia can lead to a number of serious health problems for both the mother and the baby, including premature birth, low birth weight, and even death.
- Gestational diabetes is a risk factor for pre-eclampsia. Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to develop pre-eclampsia than women without gestational diabetes.
- Pre-eclampsia can worsen the effects of gestational diabetes. Women with both gestational diabetes and pre-eclampsia are at increased risk for serious complications, such as premature birth and low birth weight.
- Pre-eclampsia can be treated with medication. There are a number of medications that can be used to treat pre-eclampsia. These medications can help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of serious complications.
- Pre-eclampsia can be prevented. There are a number of things that women can do to help prevent pre-eclampsia, including eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking prenatal vitamins.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to be aware of the risks of pre-eclampsia. Talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk and monitor for signs and symptoms of pre-eclampsia.
Macrosomia – This is a condition in which the baby is born with a high birth weight. Macrosomia can increase the risk of complications during delivery, such as shoulder dystocia and birth injuries.
Macrosomia is a condition that can occur when a baby is born with a high birth weight. This can be caused by a number of factors, including gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the placenta producing hormones that can make it difficult for the body to use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells.
When the body can’t use insulin properly, blood sugar levels can get too high. This can lead to a number of complications during pregnancy, including macrosomia.
Macrosomia can increase the risk of complications during delivery. These complications can include:
- Shoulder dystocia – This is a condition that occurs when the baby’s shoulder gets stuck behind the mother’s pubic bone during delivery.
- Birth injuries – These are injuries that can occur to the baby during delivery. Birth injuries can include bruises, cuts, and broken bones.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to manage your blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of macrosomia and other complications.
Premature birth – This is when the baby is born before 37 weeks of gestation. Premature babies are at risk for a number of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the placenta producing hormones that can make it difficult for the body to use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells.
When the body can’t use insulin properly, blood sugar levels can get too high. This can lead to a number of complications during pregnancy, including premature birth.
Premature birth is a serious problem that can have lifelong consequences for the baby. Premature babies are at risk for a number of health problems, including:
- Respiratory problems – Premature babies’ lungs are not fully developed, so they may have difficulty breathing.
- Feeding difficulties – Premature babies may have difficulty sucking and swallowing, so they may not be able to get enough nutrition.
- Developmental delays – Premature babies may have developmental delays in areas such as language, motor skills, and cognitive skills.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to manage your blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of premature birth. This can be done by eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking insulin if necessary.
Premature birth is a serious complication of gestational diabetes, but it can be prevented with proper management.
Cesarean delivery – This is a surgical procedure to deliver the baby. Cesarean delivery may be necessary if the mother has gestational diabetes and is at risk for complications during delivery.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the placenta producing hormones that can make it difficult for the body to use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells.
When the body can’t use insulin properly, blood sugar levels can get too high. This can lead to a number of complications during pregnancy, including Cesarean delivery.
- Cesarean delivery is a surgical procedure to deliver the baby. It is typically performed when vaginal delivery is not possible or safe. Cesarean delivery may be necessary if the mother has gestational diabetes and is at risk for complications during delivery.
- Cesarean delivery is a major surgery. It is important to be aware of the risks and benefits of cesarean delivery before making a decision about whether or not to have one.
-
The risks of cesarean delivery include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Damage to the uterus or other organs
-
The benefits of cesarean delivery include:
- Reducing the risk of complications during delivery
- Delivering the baby safely and quickly
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of cesarean delivery.
Insulin therapy – This is a treatment for gestational diabetes that involves taking insulin to help control blood sugar levels.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the placenta producing hormones that can make it difficult for the body to use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells.
When the body can’t use insulin properly, blood sugar levels can get too high. This can lead to a number of complications during pregnancy, including pre-eclampsia, macrosomia, premature birth, and cesarean delivery.
Insulin therapy is a treatment for gestational diabetes that involves taking insulin to help control blood sugar levels. Insulin therapy can help to reduce the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery.
Insulin therapy is typically given by injection. The dose of insulin will vary depending on the individual’s blood sugar levels.
Insulin therapy is a safe and effective treatment for gestational diabetes. It can help to reduce the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery.
If you have gestational diabetes, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. This plan may include insulin therapy, diet, and exercise.
Diet and exercise – These are important parts of managing gestational diabetes. Eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise can help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the placenta producing hormones that can make it difficult for the body to use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells.
When the body can’t use insulin properly, blood sugar levels can get too high. This can lead to a number of complications during pregnancy, including pre-eclampsia, macrosomia, premature birth, and cesarean delivery.
Diet and exercise are important parts of managing gestational diabetes. Eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
- Eating a healthy diet means eating foods that are low in sugar and carbohydrates. This will help to keep your blood sugar levels from getting too high.
- Getting regular exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor about a diet and exercise plan that is right for you. By following your doctor’s instructions, you can help to manage your gestational diabetes and reduce your risk of complications.
Monitoring blood sugar levels – This is important for managing gestational diabetes. Blood sugar levels should be checked regularly to make sure they are within a healthy range.
Monitoring blood sugar levels is an important part of managing gestational diabetes. By checking your blood sugar levels regularly, you can make sure that they are within a healthy range and reduce your risk of developing complications. High blood sugar levels can lead to a number of problems, including pre-eclampsia, macrosomia, premature birth, and cesarean delivery. By keeping your blood sugar levels under control, you can help to reduce your risk of these complications and have a healthy pregnancy.
If you have gestational diabetes, your doctor will recommend that you check your blood sugar levels several times a day. You will need to use a blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar levels. Your doctor will teach you how to use the meter and how to interpret your results. It is important to check your blood sugar levels regularly, even if you are feeling well. High blood sugar levels can develop without any symptoms.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is an important part of managing gestational diabetes. By keeping your blood sugar levels under control, you can reduce your risk of developing complications and have a healthy pregnancy.
FAQs about Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. Some of these complications can potentially impact the health of both the mother and the baby.
Question 1: What causes gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is caused by the placenta, which produces hormones that can make it difficult for the body to use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes often does not cause any symptoms. However, some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Question 3: How is gestational diabetes diagnosed?
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed with a glucose tolerance test. This test measures how well your body uses glucose. The test is usually performed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Question 4: How is gestational diabetes treated?
Gestational diabetes is treated with diet, exercise, and medication. Diet and exercise can help to control blood sugar levels. Medication may be necessary if diet and exercise are not enough to control blood sugar levels.
Question 5: What are the risks of gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. These complications can include pre-eclampsia, macrosomia, premature birth, and cesarean delivery.
Question 6: Can gestational diabetes be prevented?
There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes. However, there are some things that you can do to reduce your risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on the health of both the mother and the baby. However, by following your doctor’s instructions, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and reduce your risk of complications.
Transition to the next article section:
If you have any questions about gestational diabetes, please talk to your doctor.
Tips for Managing Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. Some of these complications can potentially impact the health of both the mother and the baby. By following these tips, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and reduce your risk of complications.
Tip 1: Eat a healthy diet.
Eating a healthy diet is one of the most important things you can do to manage gestational diabetes. A healthy diet for gestational diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also includes lean protein and low-fat dairy products. Limit your intake of sugary foods, processed foods, and saturated and unhealthy fats.
Tip 2: Get regular exercise.
Exercise can help you control your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of gestational diabetes complications. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Some good choices for exercise during pregnancy include walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga.
Tip 3: Monitor your blood sugar levels.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is an important part of managing gestational diabetes. By checking your blood sugar levels regularly, you can make sure that they are within a healthy range. Your doctor will tell you how often to check your blood sugar levels and what your target range is.
Tip 4: Take medication if necessary.
If diet and exercise are not enough to control your blood sugar levels, you may need to take medication. There are several different types of medication that can be used to treat gestational diabetes. Your doctor will work with you to choose the best medication for you.
Tip 5: Follow your doctor’s instructions.
It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Your doctor will give you specific instructions on how to manage your gestational diabetes. By following your doctor’s instructions, you can help reduce your risk of complications and have a healthy pregnancy.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By following these tips, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and reduce your risk of complications. Eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and monitoring your blood sugar levels are all important parts of managing gestational diabetes. If diet and exercise are not enough to control your blood sugar levels, you may need to take medication. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By following these tips, you can help reduce your risk of complications and have a healthy pregnancy.
Conclusion
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on the health of both the mother and the baby. However, by following your doctor’s instructions, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and reduce your risk of complications. This includes eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and monitoring your blood sugar levels. If diet and exercise are not enough to control your blood sugar levels, you may need to take medication.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By following these tips, you can help reduce your risk of complications and have a healthy pregnancy.
Youtube Video: